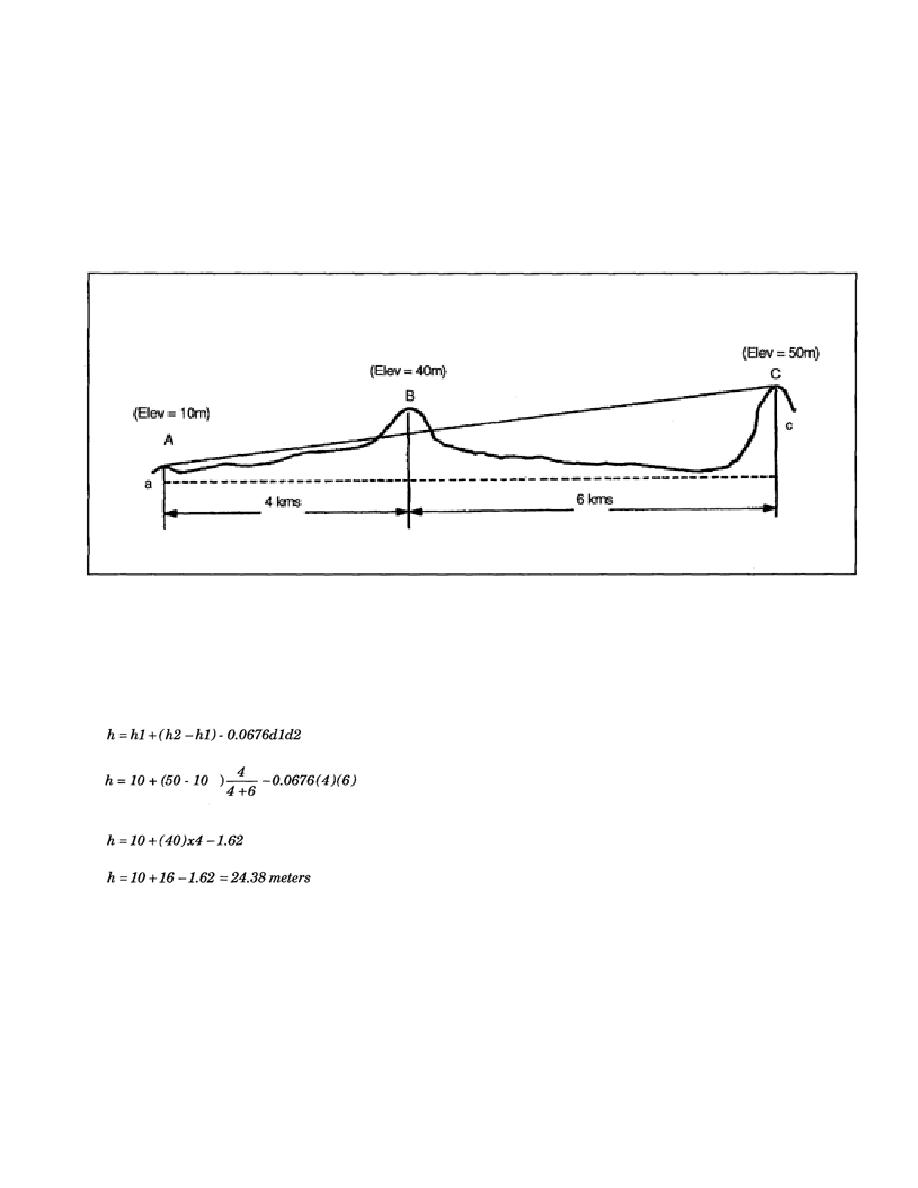
B, and add this to the true elevation of B above the chord ac. This is the effective elevation. This is done
using the following formula:
h = 0.0676d1d2
h = 0.0676 x 4 x 6
h = 1.62 kilometers
Figure 2-7. The Effect of Curvature at an Intermediate Obstruction
The effective elevation of B is 40 + 1.62 = 41.62 meters. To perform the next step, compute the
effective elevation of the grade line from the ground at A to the ground at C where it passes through the
vertical of B. Use the principle of similar triangles as follows:
Therefore, the amount of obstruction at B is 41.62 - 24.38 = 17.24 meters.
f. The computation of obstruction is essentially the solution of similar triangles. In a), Figure 2-8,
the elevations of the points are A = 293 meters, B = 298 meters, and obstruction H = 294 meters. The
distance from A to H is 8 kilometers and from B to H is 6 kilometers. Refer to Table 2-1, page 2-31,
and locate the effective elevations of points H and B. The effective elevation of H is 294.0 - 4.3 = 289.7
meters and B is 298.0 - 13.2 = 284.8 meters.
2-33
EN0593



 Previous Page
Previous Page
