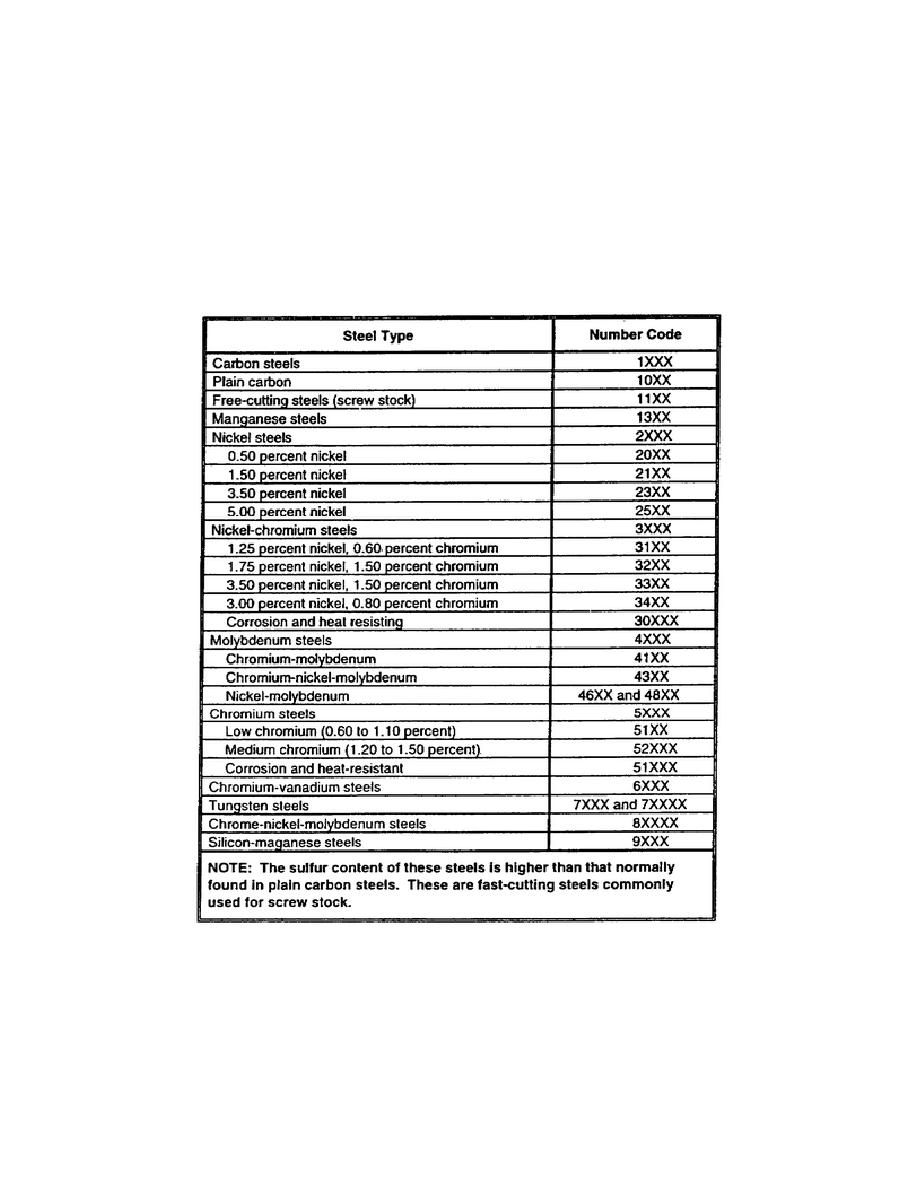
steel. The first digit, 2, indicates the main alloy element; in this case, nickel. The second digit, 3,
indicates the percentage of the main alloy element other than carbon; thus, there is 3 percent nickel. The
last two digits in the number indicate the amount of carbon expressed in hundredths of percent; the
example indicates that the steel has 0.30 percent carbon. In the case of a five-digit number, the second
and third digits are used to express the percent of the main alloy element when this figure requires more
than one digit; for example, 1.50 percent and 18.00 percent. In the case of plain carbon steel, 1095, the
same system of interpreting numbers is used except that the digit 1 represents carbon steel, and since
there is no main alloy element other than carbon, the second digit is always 0.
Table 5-4. Steel identification numerical index
(2) Color-code system. This system is linked to the numerical system of identifying the
various alloys and is used to mark them. At present, there are two color-code systems in use for
identifying metals and alloys. The old SAE-AISI system is related primarily to steel metals; however,
the new system changes the old system and adds aluminum and copper alloys.
5-19
EN0562



 Previous Page
Previous Page
