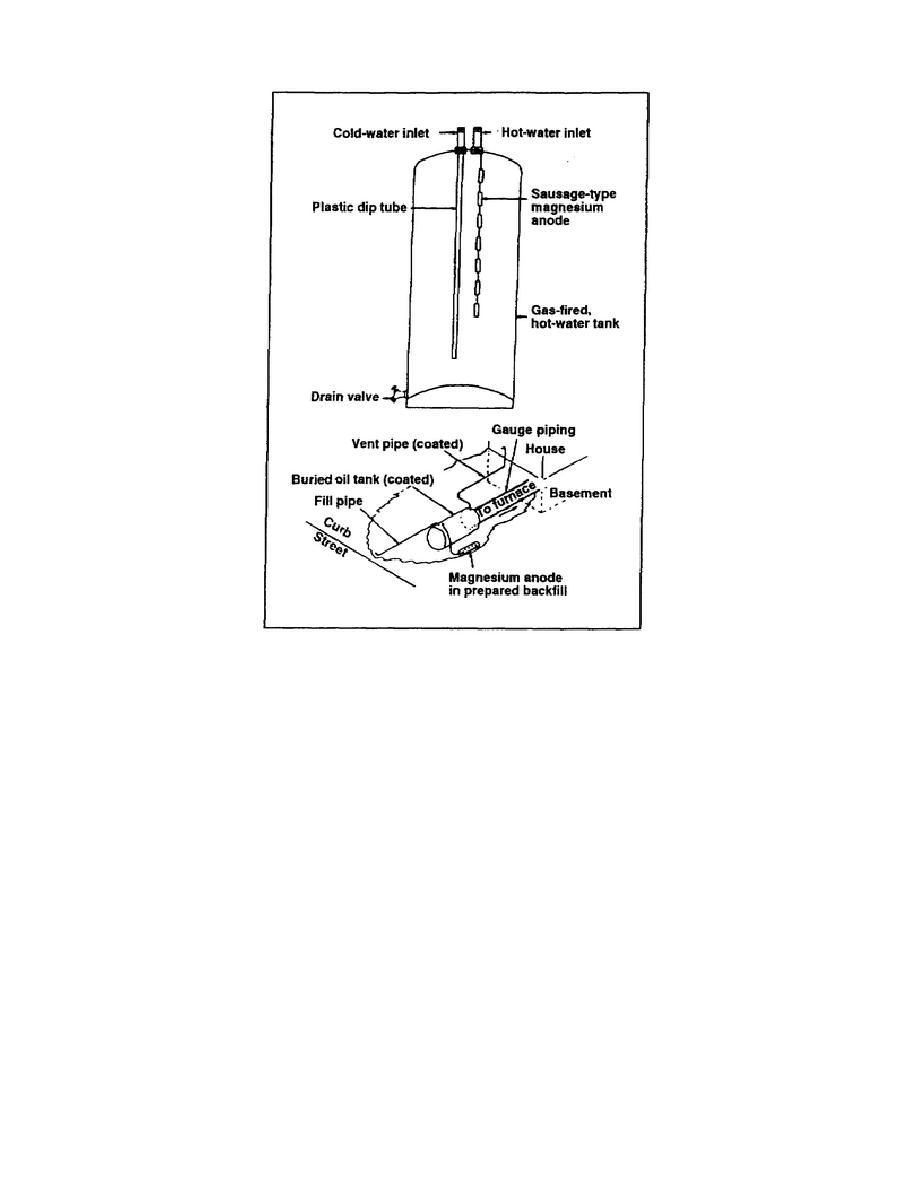
Figure 5-10. Galvanic cathodic protection
(2) Impressed current method. The impressed current method of cathodic protection is
designed to protect large metal structures that are located in corrosive areas. An alternating current
source is required with this protection method. In addition, a rectifier is necessary to obtain the required
direct-current potential. The basic principal of the impressed current method is merely the application of
the galvanic-celled reaction. The component parts of this method are the-
Cathode (cathodic area), which is the metal structure to be protected.
Anode (anodic area), which is composed of suitable anodic material.
Electrolyte (or ground), which is the ionized corrosive material.
Rectifier and various connections, which complete the electrical current.
The operation of this method depends on a rectifier that forces direct electrical current from the anode
through the electrolyte to the metal structure that needs protection. This method causes the metal
structure to be the cathode, suppresses all anodic currents from
5-17
EN0562



 Previous Page
Previous Page
