PART B: MIXING AND PREPARING
PROTECTIVE COATINGS
Now that you have a basic knowledge of the types of protective coatings, you are about to undertake the
most important task of the trade--mixing and preparing the protective coatings.
2-8. Mixing, Coloring, and Tinting Paints. Coloring and tinting paint is not difficult when a new
mixture of paint is first made; however, when you attempt to match paint already applied on a surface, it
is difficult because paint changes shades after drying and aging. Coloring and tinting paint is a matter of
trial and error. To be a professional protective-coating specialist, it is necessary that you understand the
color combinations, color mixing, tinting, and color harmony. You must also understand how to mix
paint by boxing (hand mixing) and by using power equipment, how to thin paint, and the special
procedures required for mixing aluminum paint.
a. Color Combinations. Skillful mixing of colors is one of the most important aspects of
painting and decorating, especially in interior decorating. The 12 colors found on a color wheel are
grouped as primary, secondary, and tertiary.
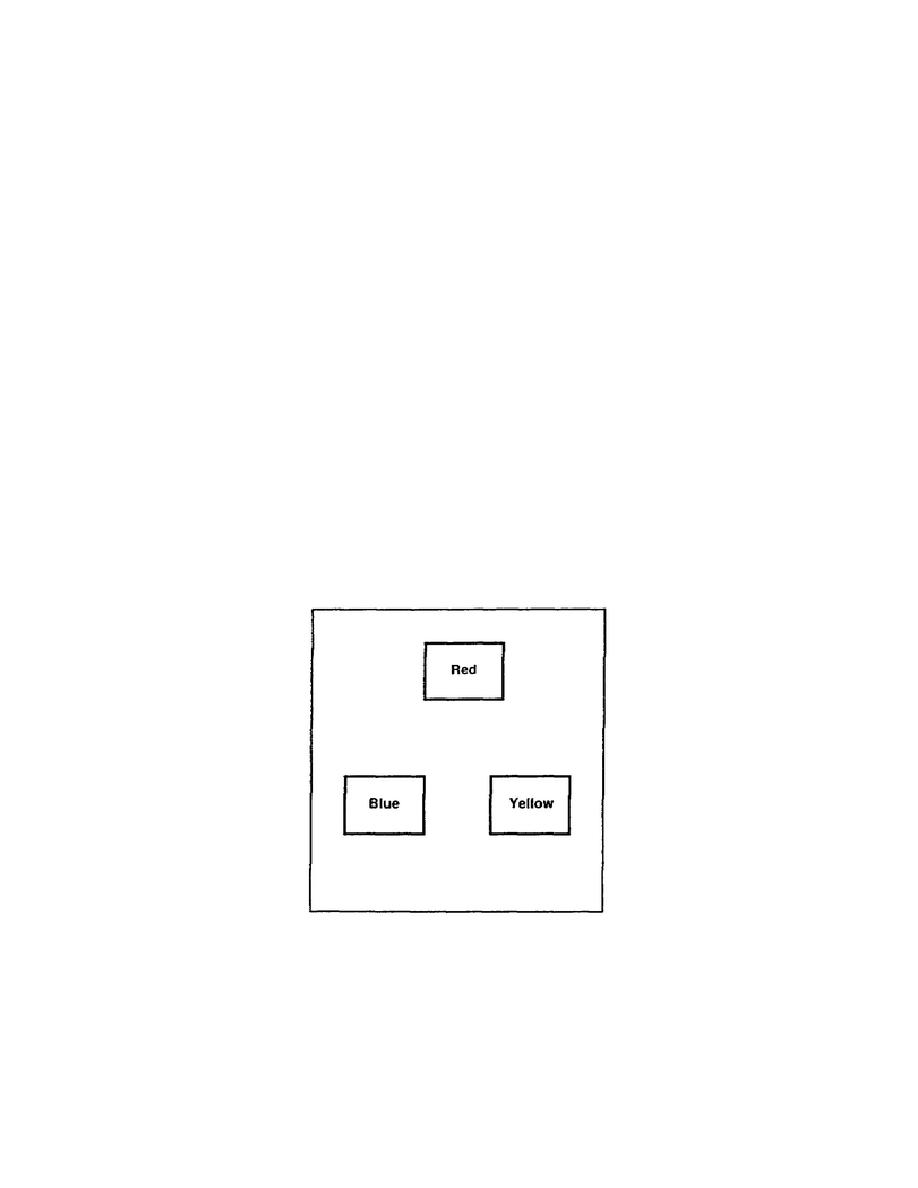
(1) Primary colors. There are three primary colors (Figure 2-1). They are blue, red, and
yellow.
(2) Secondary colors. Secondary colors (Figure 2-2, page 2-14) are made by mixing any two
of the primary colors together. For instance, yellow and red form orange; red and blue form purple; and
blue and yellow form green.
Figure 2-1. Primary colors
2-13
EN0562



 Previous Page
Previous Page
