TC 9-62
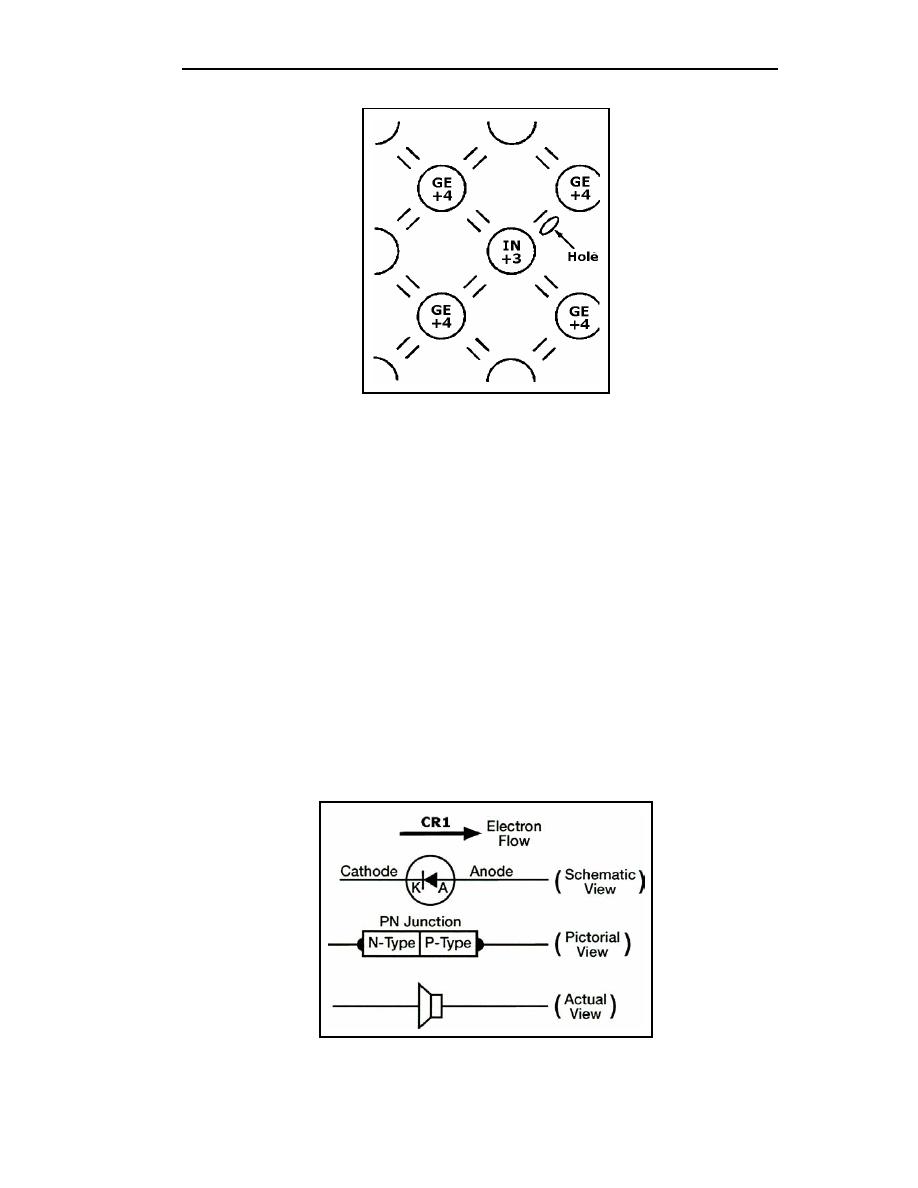
Figure 1-11. Germanium Crystal Doped With Indium
SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE
1-57. Joining a section of N-type semiconductor material with a similar section of
P-type semiconductor material, will obtain a device known as a PN JUNCTION. The area
where the N and P regions meet is appropriately called the junction. The unusual
characteristic of this device makes it extremely useful in electronics as a diode rectifier.
The diode rectifier or PN junction diode performs the same function as its counterpart in
electron tubes but in a different way. The diode is nothing more than a two-element
semiconductor device that makes use of the rectifying properties of a PN junction to
convert AC into DC by permitting current flow in only one direction. Figure 1-12 shows
the schematic symbol of a PN junction diode. The vertical bar represents the cathode (N
type material) since it is the source of electrons. The arrow represents the (P-type material)
since it is the destination of the electrons. The label "CR1" is an alphanumerical code used
to identify the diode. Figure 1-12 shows only one diode, so it is labeled CR1 (crystal
rectifier number one). If there were four diodes shown, then the last diode would be labeled
CR4. The heavy dark line shows electron flow (notice it is against the arrow). For further
clarification, a pictorial view of a PN junction and an actual view of a semiconductor (one
of many types) are also shown.
Figure 1-12. PN Junction Diode
1-16
TC 9-62
23 June 2005



 Previous Page
Previous Page
