buildings. These materials are frequently referred to
as "wall board." They are normally stocked at depots
and are component parts of many of the issue
prefabricated buildings.
3-3.
ROOF SHEATHING
a. All flexible roof coverings such as roll
roofing and asphalt shingles require a continuous
supporting surface.
Rigid, large-panel roofing
materials, such as corrugated sheet metal and
asbestos boards do not require continuous support
except that, in extremely cold climates, solid
sheathing is recommended for its insulating value.
b. Wood sheathing should be seasoned
wood ranging in nominal size from 1 x 4 to 1 x 8. If
the roof is sheathed solid the sheathing may be square
edged, tongued and grooved, or shiplapped. It should
Figure 3-1. Slatted sheathing.
be surfaced on both edges and at least one side. It
should be nailed with two or more 8-penny nails to
corrugated sheet metal and prepared roofing.
a. Corrugated sheet-metal roofing.
are staggered to prevent weak spots in the roof. After
Standard corrugated sheet-metal covering has
the roof has been sheathed, cutting lines are marked
corrugations 2 1/2 inches wide and 5/8 inch deep.
by snapping a chalkline. Then the ends of the
The sheets are 26 inches wide and vary in length
sheathing are cut off smooth, preferably with a power
from 6 to 12 feet. If steel they are either painted or
saw, leaving the correct amount of overhang. If there
galvanized to prevent corrosion.
Corrugated
is no overhang the cut in made flush with the outside
aluminum requires no coating.
edge of the end rafter.
b. Prepared roofing. There are several
c. Where corrugated sheet metal or other
brands of prepared roofing, a similar in type. They
strong, large-panel material is used for roof covering,
are composed of either paper, felt, or asbestos paper,
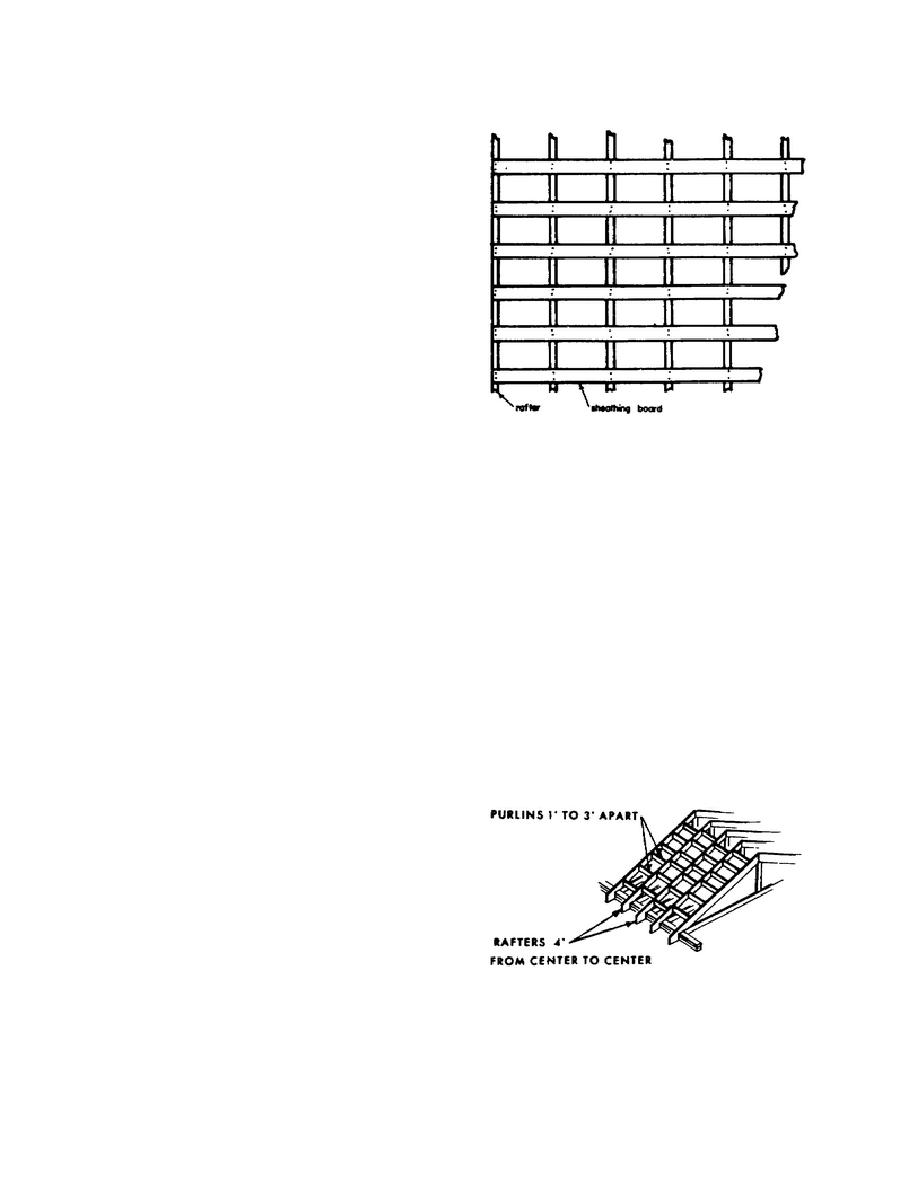
slatted sheathing may be used as an economy
and are saturated with different brands of
measure if extra insulation in not required and if the
waterproofing compounds. They are assembled at
rafter spacing is moderate. "One-in-three" spacing,
the factory, along with roofing nails and asphalt
in which the spaces left between the sheathing boards
cement, into strips about 1 yard wide and 12 yards
are twice the width of the boards (fig. 3-1), is
long. The roofings used in TO construction usually
common practice. Where rafters are very widely
have a plain surface treated with sand, mica, or talc to
spaced (2 feet on centers (OC) and wider) the use of
prevent sticking. Other mineral surfacing includes
slate and ceramic granules.
spaced 1 to 3 feet apart (fig. 3-2) is preferable to
slatted sheathing for corrugated metal.
3-4.
TYPES OF ROOFING
Of the many types of roof covering which are
used, this subcourse covers only the types used by the
Army in the theater of operations;
Figure 3-2. Purlins.
3-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
