______________________________________________________________ Solid State Power Supplies
Therefore, if the RMS value is 115 volts AC, then the peak value would be computed as
follows:
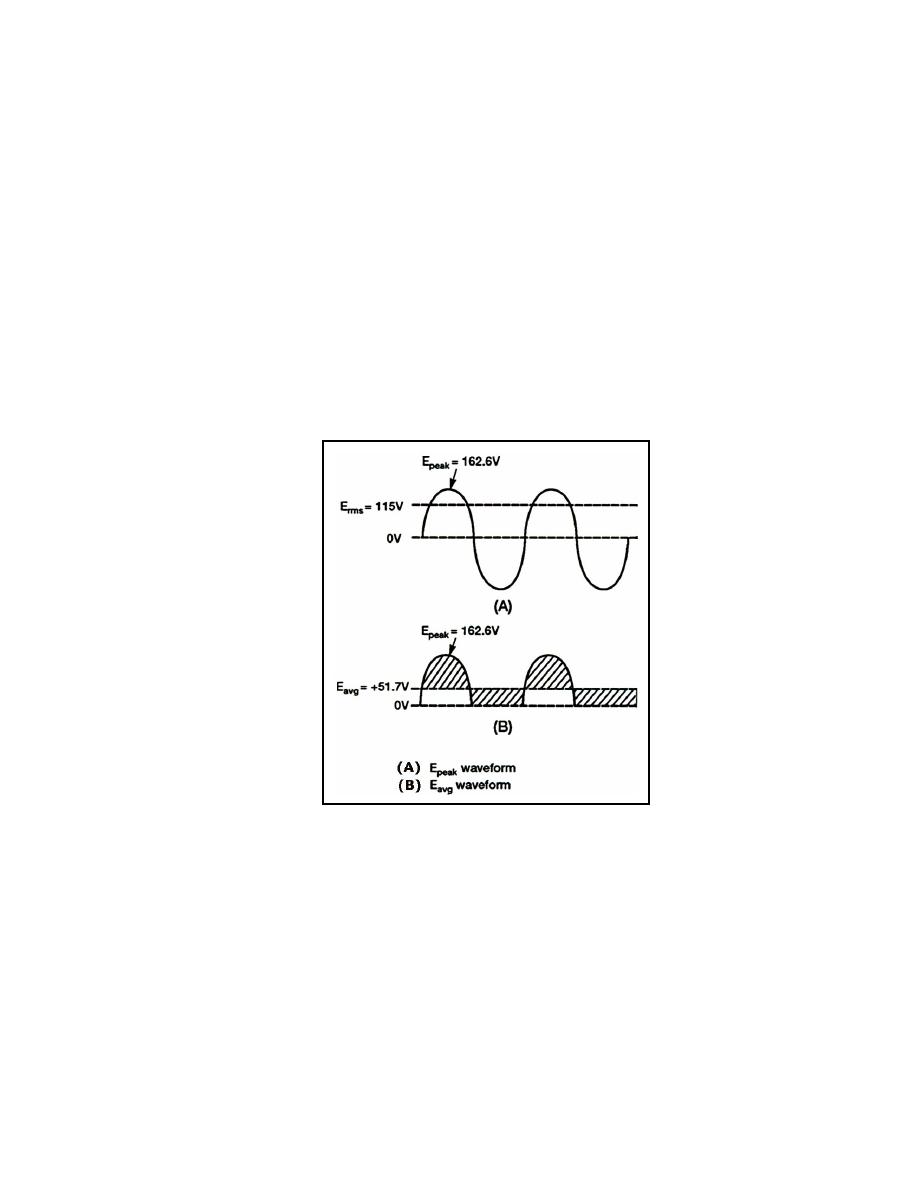
Epeak = Erms x 1.414
Epeak = 115 volts AC x 1.414
Epeak = 162.6 volts
4-11. The average value of a sine wave is 0 volts. Figure 4-4, view (B) shows how the
average voltage changes when the negative portion of the sine wave is clipped off. Since
the waveform swings positive but never negative (pass the "zero-volt" reference line), the
average voltage is positive. The average voltage (Eavg) is determined by the equation:
Eavg = Epeak x .318
Where:
So:
Eavg = 162.6 x .318
Eavg = 51.7 volts
Figure 4-4. Comparison of Epeak to Eavg in a Half-wave Rectifier
Ripple Frequency
4-12. The half-wave rectifier gets its name from the fact that it conducts during only half
the input cycle. Its output is a series of pulses with a frequency that is the same as the input
frequency. So, when operated from a 60-Hz line, the frequency of the pulses is 60 Hz. This
is called RIPPLE FREQUENCY.
Conventional Full-Wave Rectifier
4-13. A full-wave rectifier is a device that has two or more diodes arranged so that load
current flows in the same direction during each half cycle of the AC supply. Figure 4-5
shows a diagram of a simple full-wave rectifier. The transformer supplies the source
voltage for two diode rectifiers (D1 and D2). This power transformer has a center-tapped,
23 June 2005
TC 9-62
4-5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
