TC 9-62
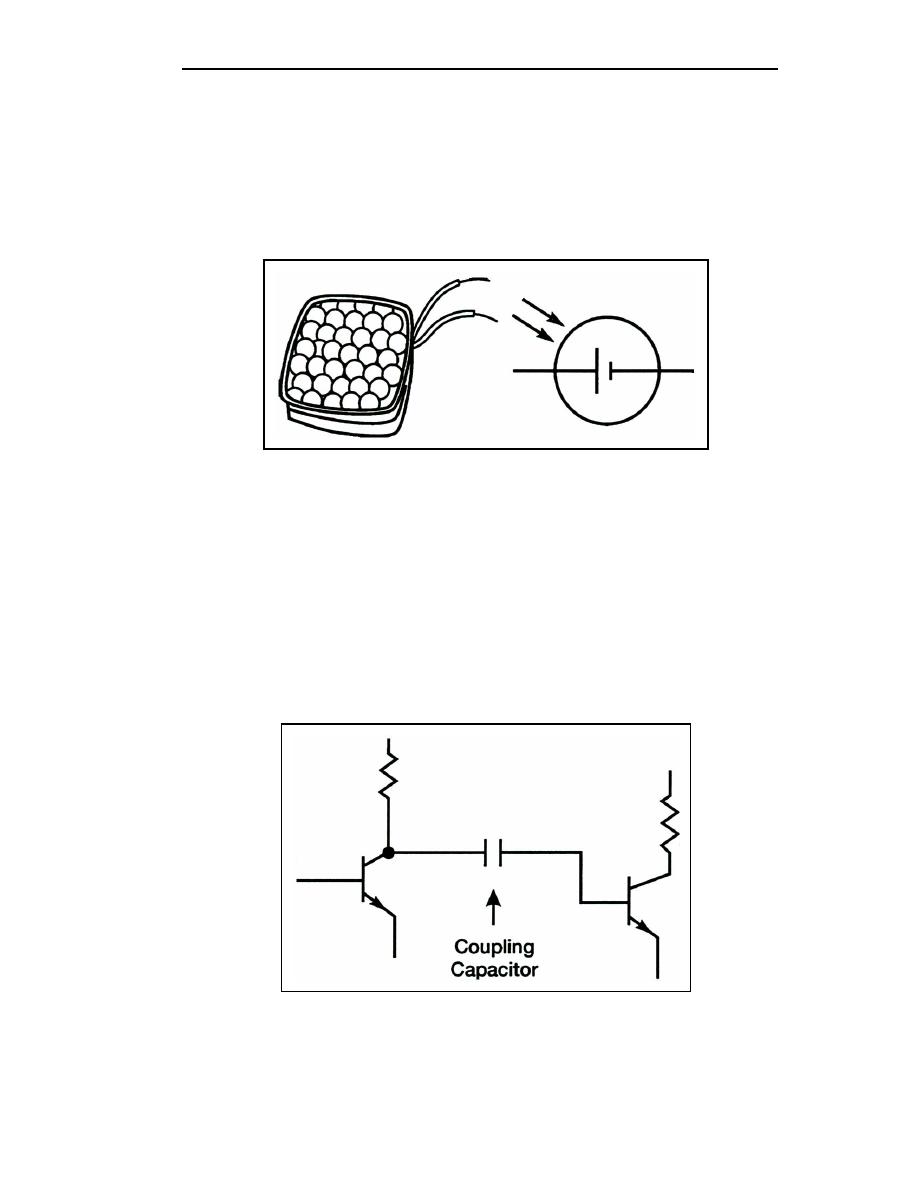
3-61. The photovoltaic cell, or SOLAR CELL, is a device that converts light energy into
electrical energy. Figure 3-35 shows an example of a solar cell and its schematic symbol.
The symbol is similar to that of a battery. The device itself acts much like a battery when
exposed to light and produces about .45 volts across its terminals, with current capacity
determined by its size. As with batteries, solar cells may be connected in series or parallel
to produce higher voltages and currents. The device is finding widespread application in
communications satellites and solar-powered homes.
Figure 3-35. Solar Cell
3-62. When it is necessary to block the voltage between one electronic circuit and
another, and transfer the signal at the same time, an amplifier coupling capacitor is often
used (see Figure 3-36). Although this method of coupling does block DC between the
circuits, voltage isolation is not complete. A newer method, making use of optoelectronic
devices to achieve electrical isolation, is the OPTICAL COUPLER (see Figure 3-37). The
coupler is composed of an LED and a photodiode contained in a light-conducting medium.
As the polarity signs in Figure 3-37 show, the LED is forward biased, while the photodiode
is reverse biased. When the input signal causes current through the LED to increase, the
light produced by the LED increases. This increased light intensity causes current flow
through the photodiode to increase. In this way, changes in input current produce
proportional changes in the output, even though the two circuits are electrically isolated.
Figure 3-36. DC Blocking With a Coupling Capacitor
3-22
TC 9-62
23 June 2005



 Previous Page
Previous Page
