Coarse aggregate should be graded up to the largest practicable size for the job conditions. According to the
American Concrete Institute (ACI) 318-83, nominal maximum size of coarse aggregate cannot be larger than one-
fifth the narrowest dimension between the sides of forms, nor one-third the depth of slabs, nor three-fourth the
minimum clear spacing between individual reinforcing bars or wires, bundles of bars, or prestressing tendons or
ducts. The type of equipment also limits the aggregate size. The 16S mixer can handle up to 3 inches of
aggregate, while the maximum size aggregate for the M919 concrete mobile is 1.5 inches. These limitations may
be waived if, in the judgment of the engineer, workability and methods of consolidation are such that concrete can
be placed without honeycomb or voids. The larger the maximum size of the coarse aggregate, the less paste
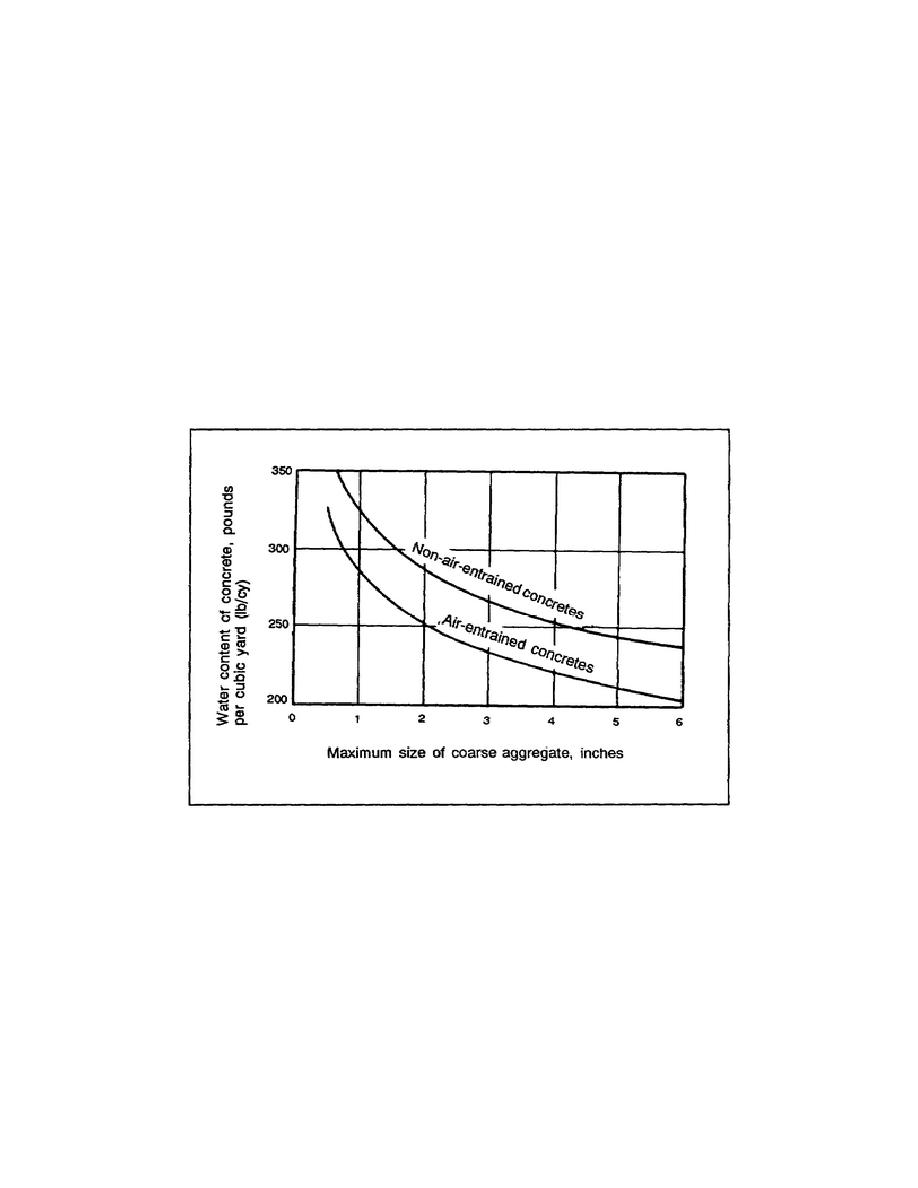
(water and cement) required to produce a given quality. Field experience shows that the amount of water required
per unit volume of concrete for a given consistency and given aggregates is nearly constant, regardless of the
cement content or relative proportions of water to cement. Further, the amount of water required decreases with
increases in the maximum size of the aggregate. The water required per cubic yard of concrete with a slump of 3
to 4 inches is shown in Figure 1-3 for a wide range of coarse-aggregate sizes. The figure demonstrates that for a
given w/c ratio, the amount of cement required decreases as the maximum size of coarse aggregate increases.
However, in some instances, especially in higher strength ranges, concrete containing smaller maximum-size
aggregate has a higher compressive strength than concrete with larger maximum-size aggregate at the same w/c
ratio.
Figure 1-3. Water requirement for concrete of a given consistency
as a function of coarse-aggregate size.
Bulk Unit Weight
The weight of the aggregate that fills a 1-cubic-foot container. This term is used because the volume contains
both aggregate and voids air spaces.
1-11
EN5466



 Previous Page
Previous Page
