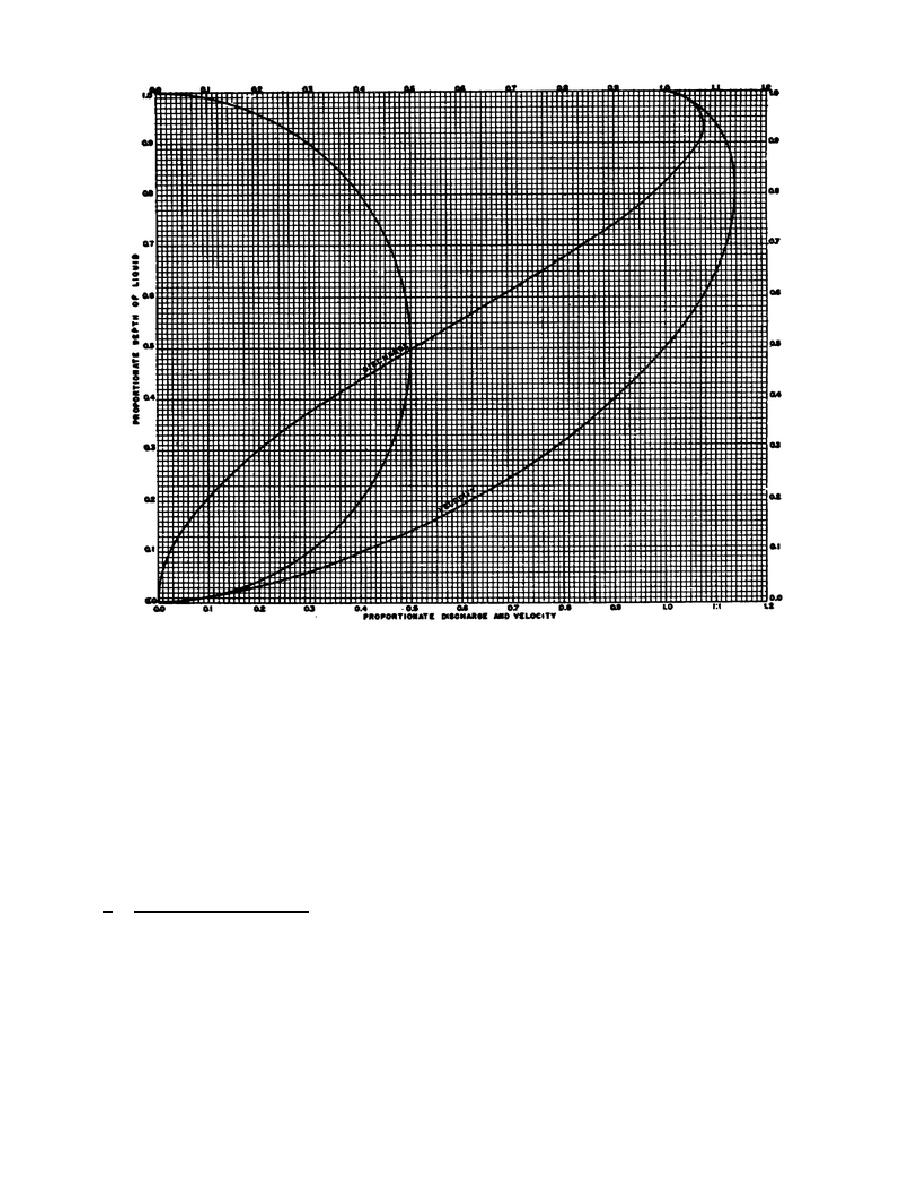
Figure 15.
Proportionate flow chart.
flow velocity.
Therefore the actual
invert at the lower manhole is the
velocity
can
be
determined
by
elevation of the invert of the upper
multiplying the velocity ratio by the
manhole less the product of the slope
full
velocity.
Continuing
the
multiplied by the length of the sewer
example, the full flow velocity was
between
manholes.
The
invert
found to be 3.2 feet per second and
elevations of the upper manhole will
the velocity ratio 1.045.
Therefore
be known for each section except the
the actual velocity will be (3.2 x
first.
The invert at the first
1.045) = 3.34 feet per second.
The
manhole will usually be made as close
actual velocity must be between 2 and
to the ground level as possible while
10 feet per second.
If lampholes are
still maintaining adequate cover.
to be used, then the velocity must be
17. SAMPLE DESIGN PROBLEM
at least 3 feet per second.
Figure
16
shows
a
plan
view
f. Invert
elevations.
Invert
and
profile
of
an
area
for
elevations can be determined once the
which
a
sewage
collection
slope is known.
The elevation of the
Figure 16.
For use with sample design (issued as separate item).
4-21



 Previous Page
Previous Page
