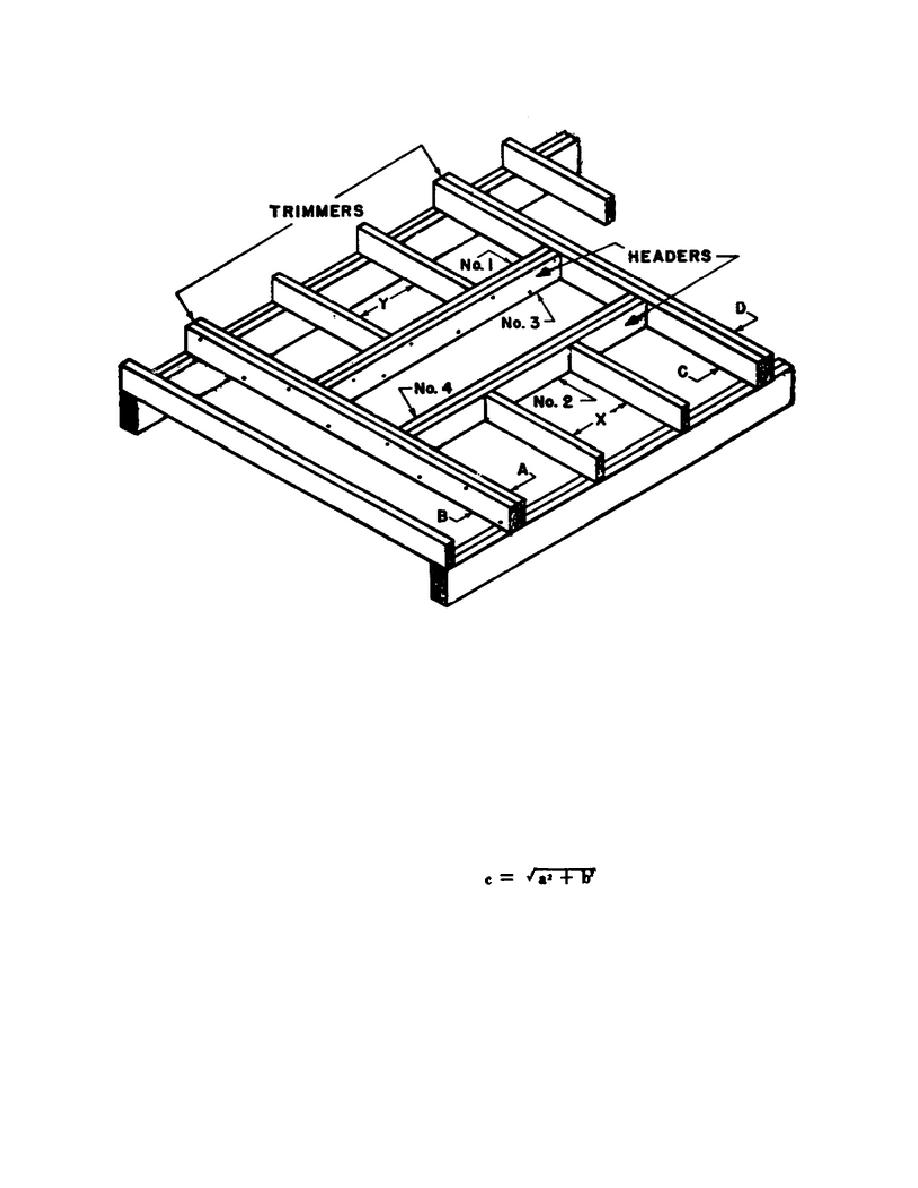
Figure 1-35. Headers and trimmers.
structure according to prepared plans and to mark the
stakes E and F by measurement and determine their
controlling points of the structure in the manner that
elevation.
is most useful to the construction force. This
c. Move transit to point D, backsight on
marking consists of indicating the corners of the
point A, turn a 90 angle, and locate and place corner
building and other horizontal and vertical positions
stakes G and H by measurement and determine their
by means of stakes, batter, boards with string-lines,
elevation.
and cut-and-fill notations.
d. Install batter boards and wire to retain
1-38. LAYING OUT A SIMPLE RECTANGLE
the layout during excavation and construction.
WITH AN ENGINEER'S TRANSIT OR
LEVELING INSTRUMENT
e. Check the squareness of the layout by
measuring the length of the diagonals, EH and FG
The procedures for a typical simple budding
and comparing it with the length computed by
layout are shown in figure 1-36.
where c is the computed diagonal
a. Establish baseline AB from a reference
length and a and b are the lengths of the two sides
monument or bench mark, or a fixed line such as a
(see calculation of diagonal, fig. 1-6).
The
street curb, and then locate point C and D on the
squareness can also be checked by using a 3 - 4 - 5
baseline by measurement.
right triangle or carpenter's square to check the 900
angle at the corners. The procedure of laying out a
b. With the transit at point C, backsight on
simple rectangle with a measuring tape is the same as
point B, turn a 90 angle, and locate and place corner
with an engineer's
1-37



 Previous Page
Previous Page
