___________________________________________________ Principles of Transmission Lines
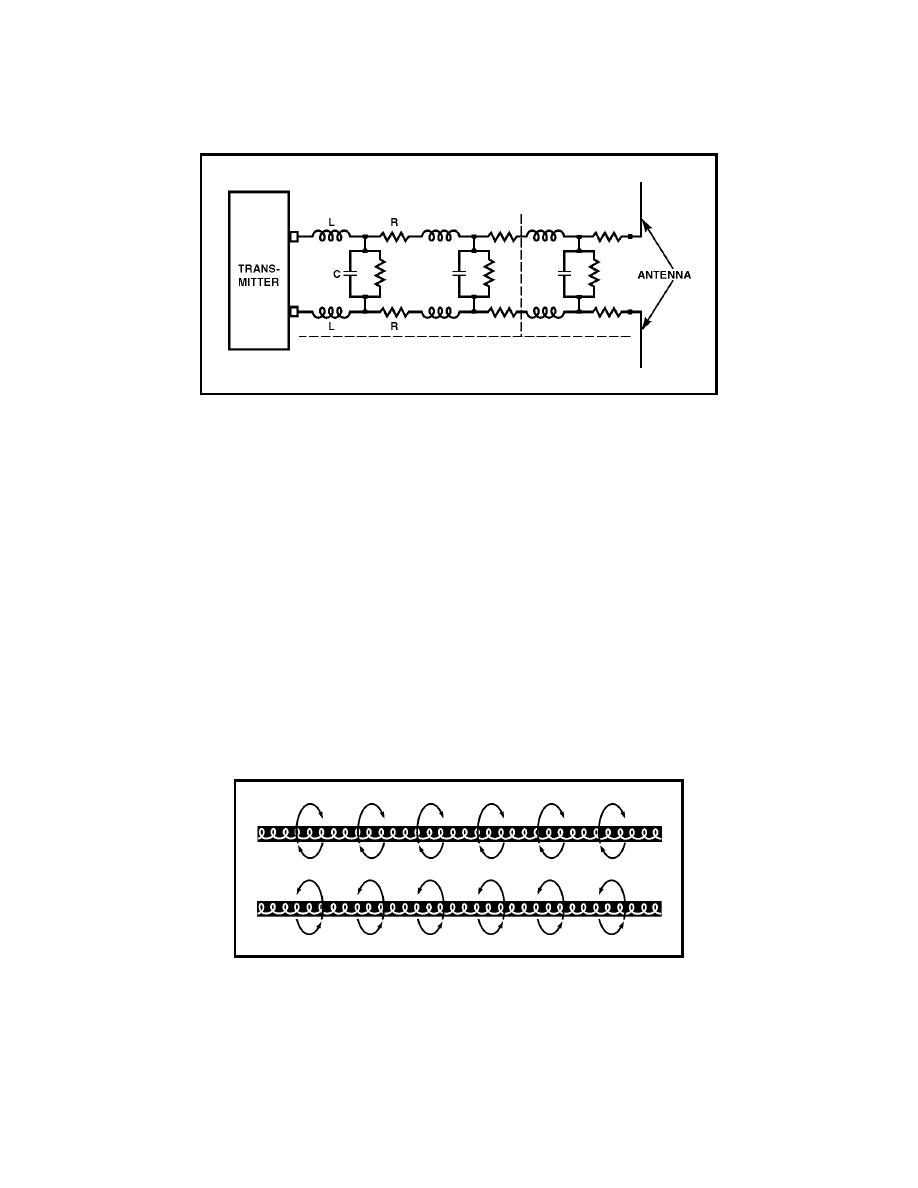
Figure 3-9. Equivalent Circuit of a Two-Wire Transmission Line
3-42. Transmission line constants, called distributed constants, are spread
along the entire length of the transmission line and cannot be distinguished
separately. The amount of inductance, capacitance, and resistance depends
on the length of the line, the size of the conducting wires, the spacing
between the wires, and the dielectric (air or insulating medium) between the
wires.
Inductance of a Transmission Line
3-43. When current flows through a wire, magnetic lines of force are set up
around the wire. As the current increases and decreases in amplitude, the
field around the wire expands and collapses accordingly. The energy
produced by the magnetic lines of force collapsing back into the wire tends to
keep the current flowing in the same direction. This represents a certain
amount of inductance, which is expressed in microhenrys per unit length.
Figure 3-10 illustrates the inductance and magnetic fields of a transmission
line.
Figure 3-10. Distributed Inductance
3-11



 Previous Page
Previous Page
