TC 9-64 _________________________________________________________________________
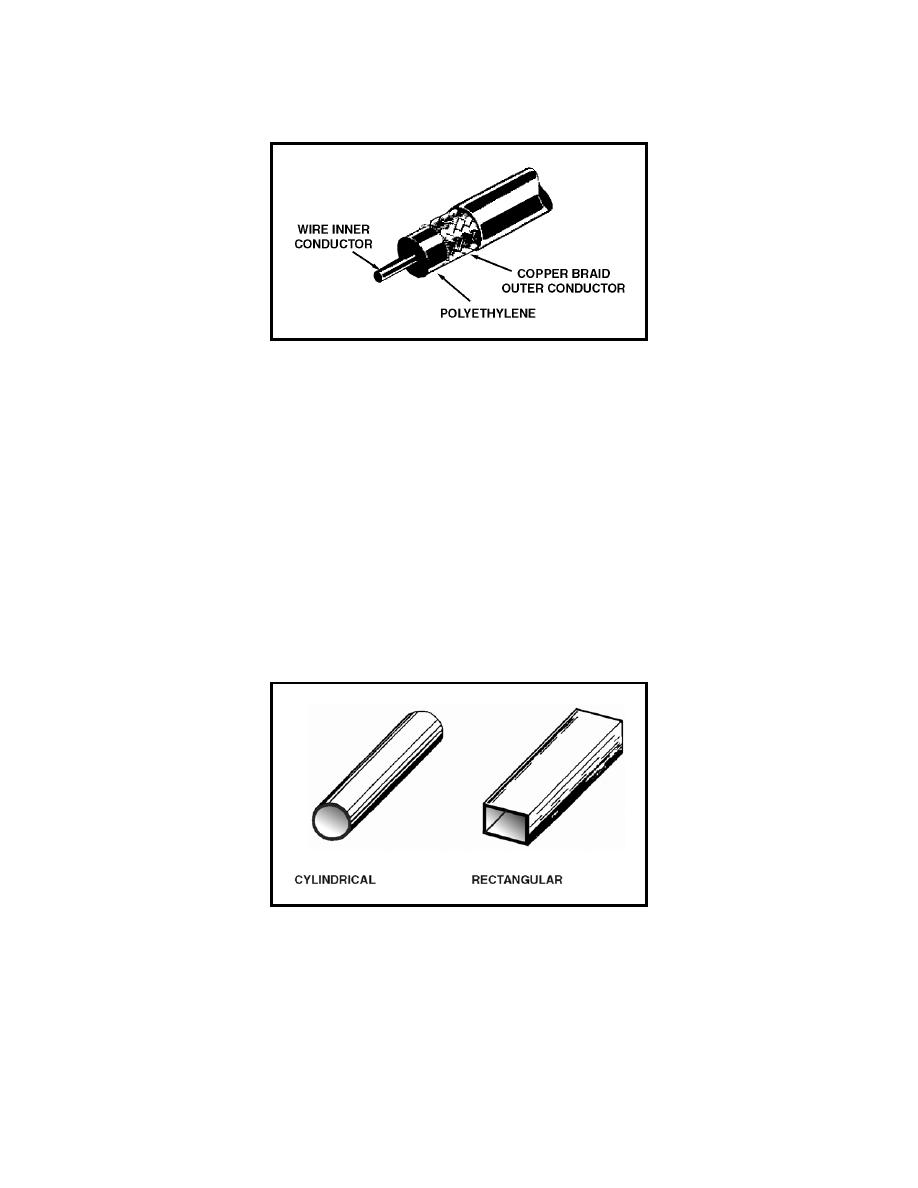
Figure 3-7. Flexible (Solid) Coaxial Line
3-19. Because of the high-frequency losses associated with rubber insulators,
polyethylene plastic was developed to replace rubber and eliminate these
losses. Polyethylene plastic is a solid substance that remains flexible over a
wide range of temperatures. It is unaffected by seawater, gasoline, oil, and
most other liquids that may be found aboard ship. The use of polyethylene as
an insulator results in greater high-frequency losses than the use of air as an
insulator. However, these losses are still lower than the losses associated
with most other solid dielectric materials.
Waveguides
3-20. The waveguide is classified as a transmission line. However, the
method by which it transmits energy down its length differs from the
conventional methods. Waveguides are cylindrical, elliptical, or rectangular
(cylindrical and rectangular shapes are shown in figure 3-8). The rectangular
waveguide is used more frequently than the cylindrical waveguide.
Figure 3-8. Waveguides
3-21. The term waveguide can be applied to all types of transmission lines in
the sense that they are all used to guide energy from one point to another.
However, usage has generally limited the term to mean a hollow metal tube or
a dielectric transmission line. In this chapter, we use the term waveguide only
to mean "hollow metal tube." It is interesting to note that the transmission of
electromagnetic energy along a waveguide travels at a velocity somewhat
slower than electromagnetic energy traveling through free space.
3-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
