TC 9-64 _________________________________________________________________________
Because of this loss by attenuation, the surface wave is impractical for long-
distance transmissions at frequencies above 2 megahertz. On the other hand,
when the frequency of a surface wave is low enough to have a very long
wavelength, the earth appears to be very small, and diffraction is sufficient
for propagation well beyond the horizon. In fact, by lowering the transmitting
frequency into the very low frequency (VLF) range and using very high-
powered transmitters, the surface wave can be propagated great distances.
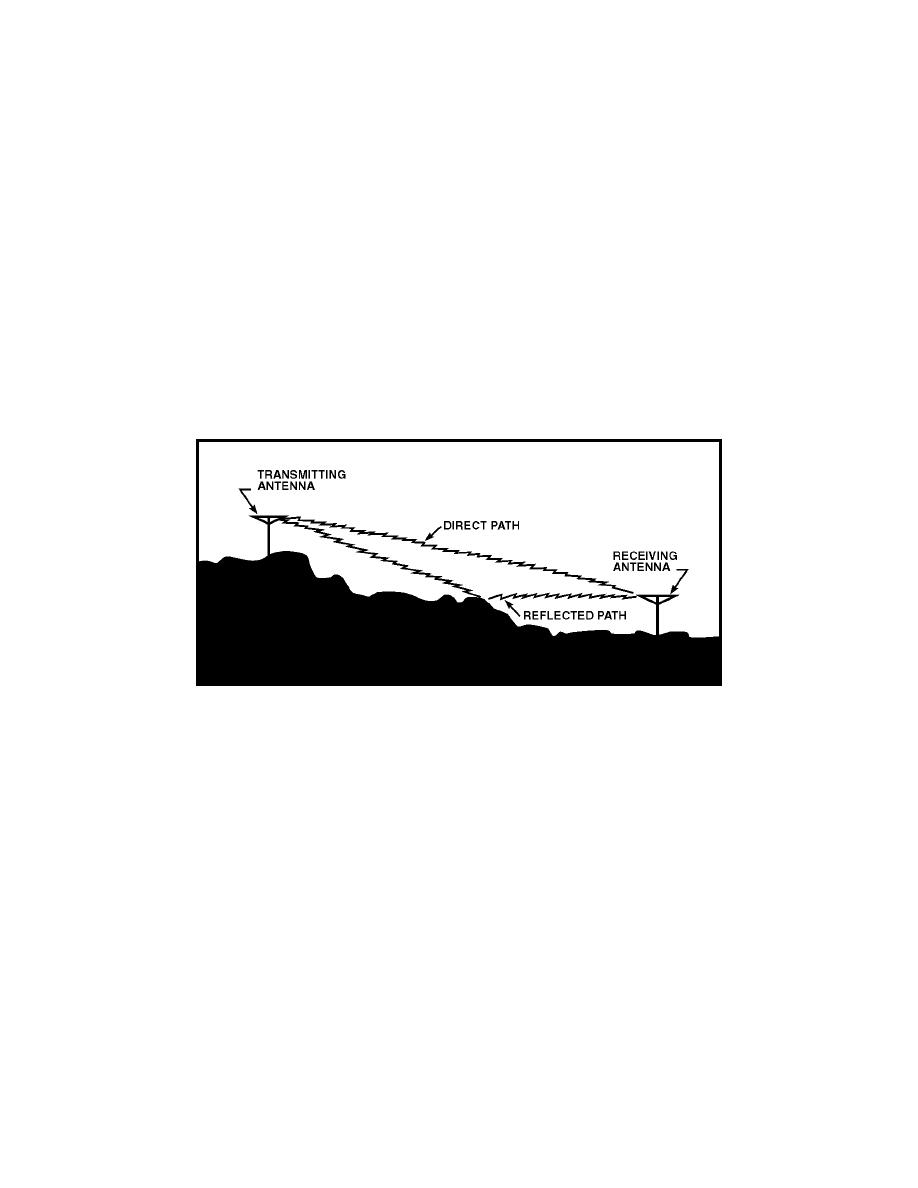
2-55. Space wave. The space wave follows two distinct paths from the
transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna--one through the air directly
to the receiving antenna, the other reflected from the ground to the receiving
antenna. These paths are illustrated in figure 2-13. The primary or direct
path of the space wave is directly from the transmitting antenna to the
receiving antenna. So, the receiving antenna must be located within the radio
horizon of the transmitting antenna. Because space waves are refracted
slightly, even when propagated through the troposphere, the radio horizon is
actually about one-third farther than the line-of-sight or natural horizon.
Figure 2-13. Space Wave Propagation
2-56. Although space waves suffer little ground attenuation, they
nevertheless are susceptible to fading. This is because space waves actually
follow two paths of different lengths (direct path and ground reflected path)
to the receiving site and, therefore, may arrive in or out of phase. If these two
component waves are received in phase, the result is a reinforced or stronger
signal. Likewise, if they are received out of phase, they tend to cancel one
another, which results in a weak or fading signal.
Sky Wave
2-57. The sky wave, often called the ionospheric wave, is radiated in an
upward direction and returned to Earth at some distant location because of
refraction from the ionosphere. This form of propagation is relatively
unaffected by the earth's surface and can propagate signals over great
distances. Usually the high frequency (HF) band is used for sky wave
propagation. The following study of the ionosphere and its effect on sky
waves will help you understand the nature of sky wave propagation.
2-18



 Previous Page
Previous Page
