__________________________________________________________ Radio Wave Propagation
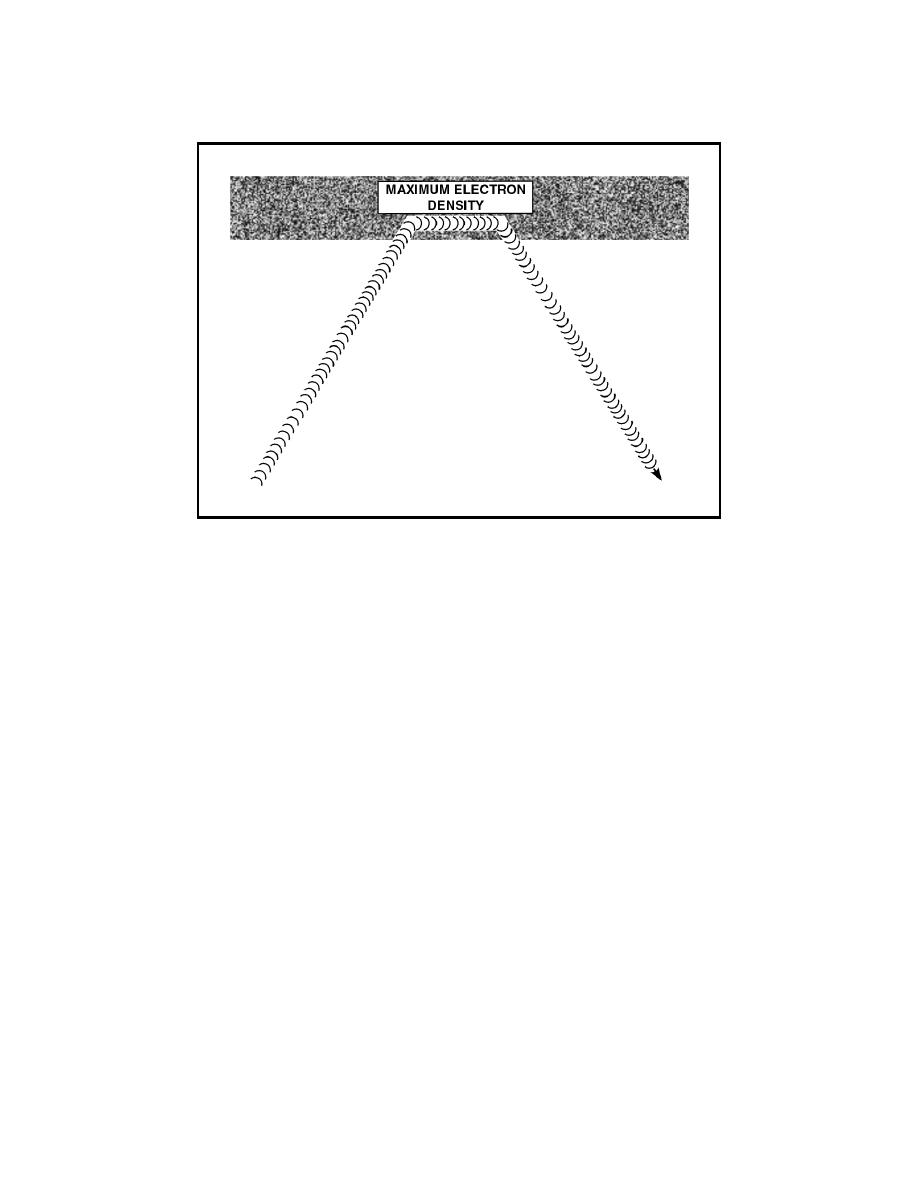
Figure 2-8. Radio Wave Refraction
2-42. Radio waves passing through the atmosphere are affected by certain
factors, such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and density. These factors
can cause the radio waves to be refracted. This effect is discussed in greater
detail later in this chapter.
Diffraction
2-43. A radio wave that meets an obstacle has a natural tendency to bend
around the obstacle, as illustrated in figure 2-9. The bending, called
diffraction, results in a change of direction of part of the wave energy from
the normal line-of-sight path. This change makes it possible to receive energy
around the edges of an obstacle as shown in figure 2-9, view A or at some
distances below the highest point of an obstruction, as shown in view B.
Although diffracted RF energy usually is weak, it can still be detected by a
suitable receiver. The principal effect of diffraction extends the radio range
beyond the visible horizon. In certain cases, by using high power and very low
frequencies, radio waves can be made to encircle the earth by diffraction.
2-13



 Previous Page
Previous Page
