TC 9-62
vacuum tube with all the other advantages of the transistor. The elements of
the FET are the gate, source, and drain which are comparable to the base,
emitter, and collector of a standard transistor.
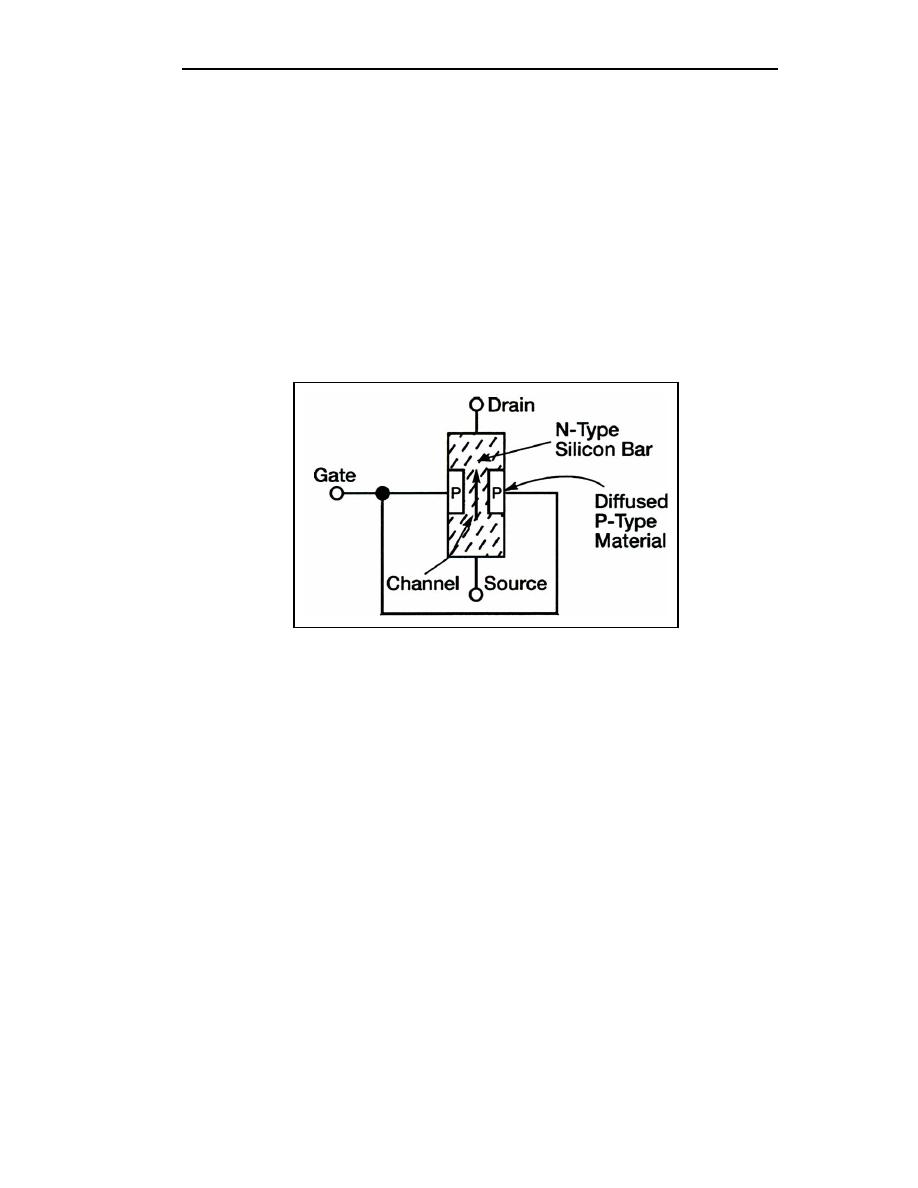
JUNCTION FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR - is made of a solid bar of either P-
or N-semiconductor material, and the gate is made of the opposite type
material. The FET is called P-channel or N-channel depending upon the type
of material used to make the bar between the source and drain. Voltage applied
to the gate controls the width of the channel and consequently controls the
current flow from the source to the drain. The JFET is normally operated with
reverse bias that controls the channel width by increasing or decreasing the
depletion region.
the gate of the MOSFET is completely insulated from the rest of the device.
The MOSFET operates in either the depletion mode or the forward-bias
enhancement mode and can be either N-channel or P-channel. The induced-
channel and the dual-gate MOSFETs are variations of the basic MOSFET.
3-40
TC 9-62
23 June 2005



 Previous Page
Previous Page
