TC 9-62
minority carriers causes a small leakage current that remains nearly constant for all reverse
voltages up to a certain value. Once this value has been exceeded, there is a sudden
increase in the reverse current. The voltage at which the sudden increase in current occurs
is called the BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE. At breakdown, the reverse current increases very
rapidly with a slight increase in the reverse voltage. Any diode can be reverse biased to the
point of breakdown, but not every diode can safely dissipate the power associated with
breakdown. A Zener diode is a PN junction designed to operate in the reverse-bias
breakdown region.
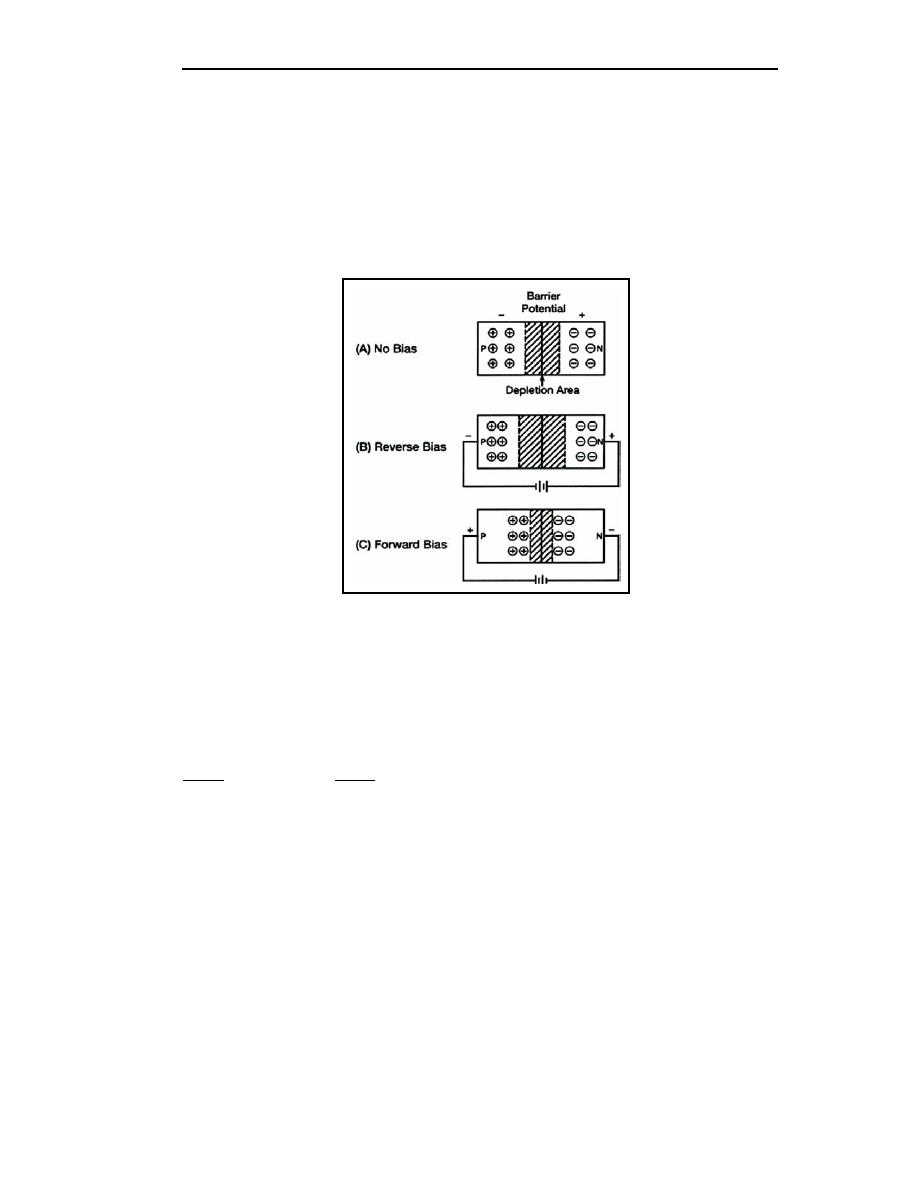
Figure 3-1. Effect of Bias on the Depletion Region of a PN Junction
3-4.
There are two distinct theories used to explain the behavior of PN junctions during
breakdown. These two theories are called ZENER EFFECT and the other is
AVALANCHE EFFECT.
3-5.
The ZENER EFFECT was first proposed by Dr. Carl Zener in 1934. According to
Dr. Zener's theory, electrical breakdown in solid dielectrics occurs by a process called
QUANTUM-MECHANICAL TUNNELING. The Zener effect accounts for the breakdown
below 5 volts, while above 5 volts the breakdown is caused by the Avalanche effect.
Although the Avalanche effect is now accepted as an explanation of diode breakdown, the
term "Zener diode" is used to cover both types.
3-6.
The true Zener effect in semiconductors can be described in terms of energy bands.
However, only the two upper energy bands are of interest. The two upper bands (see Figure
3-2, view (A)) are called the CONDUCTION BAND and the VALENCE BAND.
3-7.
The CONDUCTION BAND is a band in which the energy level of the electrons is
high enough that the electrons will move easily under the influence of an external field.
Since current flow is the movement of electrons, the readily mobile electrons in the
conduction band are capable of maintaining a current flow when an external field in the
form of a voltage is applied. Therefore, solid materials that have many electrons in the
conduction band are called conductors.
3-8.
The VALENCE BAND is a band in which the energy level is the same as the
valence electrons of the atoms. Since the electrons in these levels are attached to the atoms,
the electrons are not free to move around, as are the conduction band electrons. However,
3-2
TC 9-62
23 June 2005



 Previous Page
Previous Page
