___________________________________________________________________________ Transistors
The EMITTER, which gives off or "emits" current carriers (electrons or
holes).
The BASE, which controls the flow of current carriers.
The COLLECTOR, which collects the current carriers.
CLASSIFICATION
2-6.
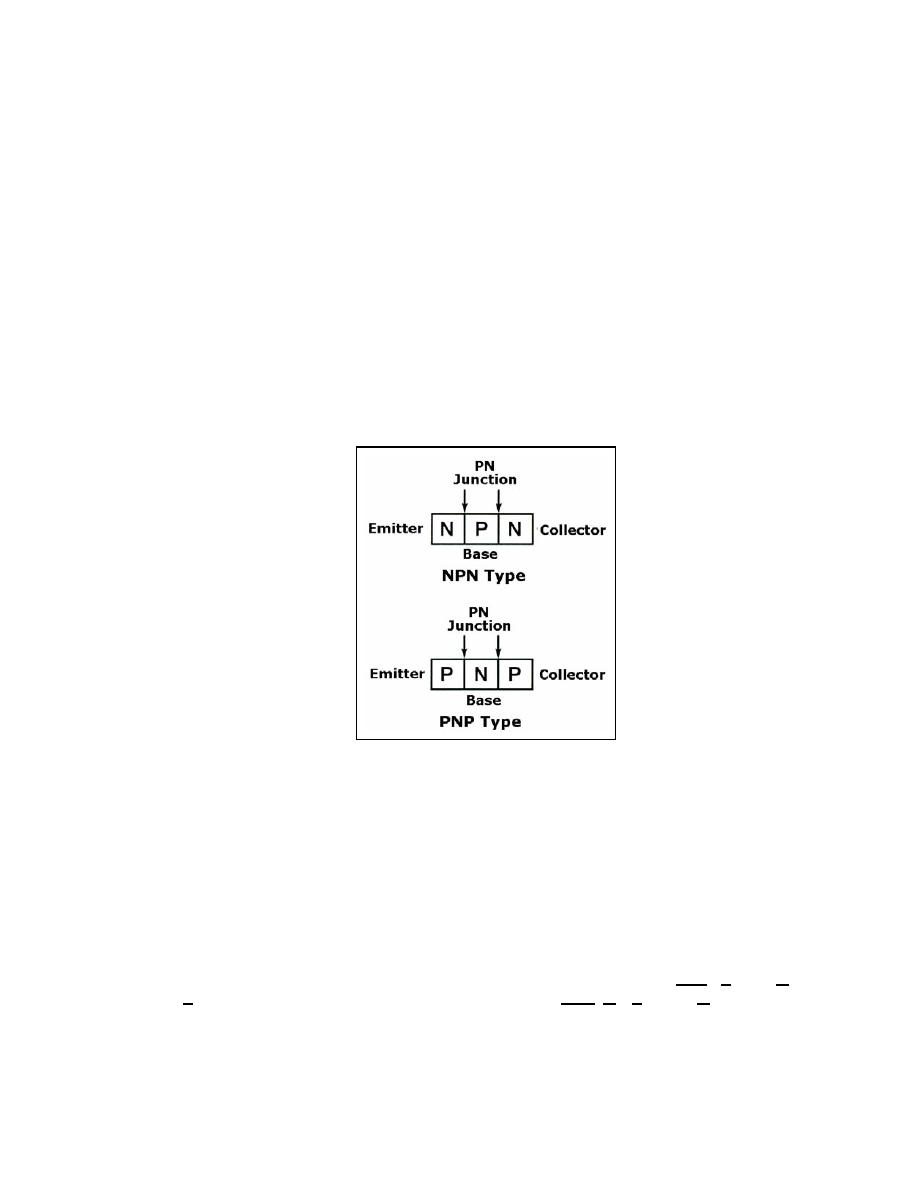
Transistors are classified, according to the arrangement of their N and P materials,
as either NPN or PNP. Their basic construction and chemical treatment is implied by their
names "NPN" or "PNP." That is, an NPN transistor is formed by introducing a thin region
of P-type material between two regions of N-type material. However, a PNP transistor is
formed by introducing a thin region of N-type material between two regions of P-type
material. Transistors constructed in this manner have two PN junctions (see Figure 2-2).
One PN junction is between the emitter and the base and the other PN junction is between
the collector and the base. The two junctions share one section of semiconductor material
so that the transistor actually consists of three elements.
Figure 2-2. Transistor Block Diagrams
2-7.
Since the majority and minority current carriers are different for N- and P-type
materials, then it stands to reason that the internal operation of the NPN and PNP
transistors will also be different. The theory of operation of the NPN and PNP transistors
will be covered separately. Any additional information about the PN junction will be given
as the theory of transistor operation is developed.
2-8.
Figure 2-3 shows the two basic types of transistors along with their circuit
symbols. Notice that the two symbols are different. The horizontal line represents the base,
the angular line with the arrow on it represents the emitter, and the other angular line
represents the collector. The direction of the arrow on the emitter distinguishes the NPN
from the PNP transistor. If the arrow points in, the transistor is a PNP (Points iN
Permanently). If the arrow points out, the transistor is an NPN (Not Pointing iN).
2-9.
Remember that the arrow always points in the direction of hole flow or from the P
to N sections (no matter whether the P section is the emitter or base) However, electron
flow is always toward or against the arrow, just like in the junction diode.
23 June 2005
TC 9-62
2-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
