_________________________________________________________________ Semiconductor Diodes
CONDUCTION PROCESS IN A SEMICONDUCTOR - accomplished by two
different types of current flow (HOLE FLOW and ELECTRON FLOW). Hole
flow is very similar to electron flow except that holes (positive charges) move
toward a negative potential and in an opposite direction to that of the electrons.
In an INTRINSIC semiconductor (one which does not contain any impurities),
the number of holes always equals the number of conducting electrons.
impurities, are added to semiconductors to increase their current flow.
Semiconductors that undergo this treatment are referred to as EXTRINSIC
SEMICONDUCTORS.
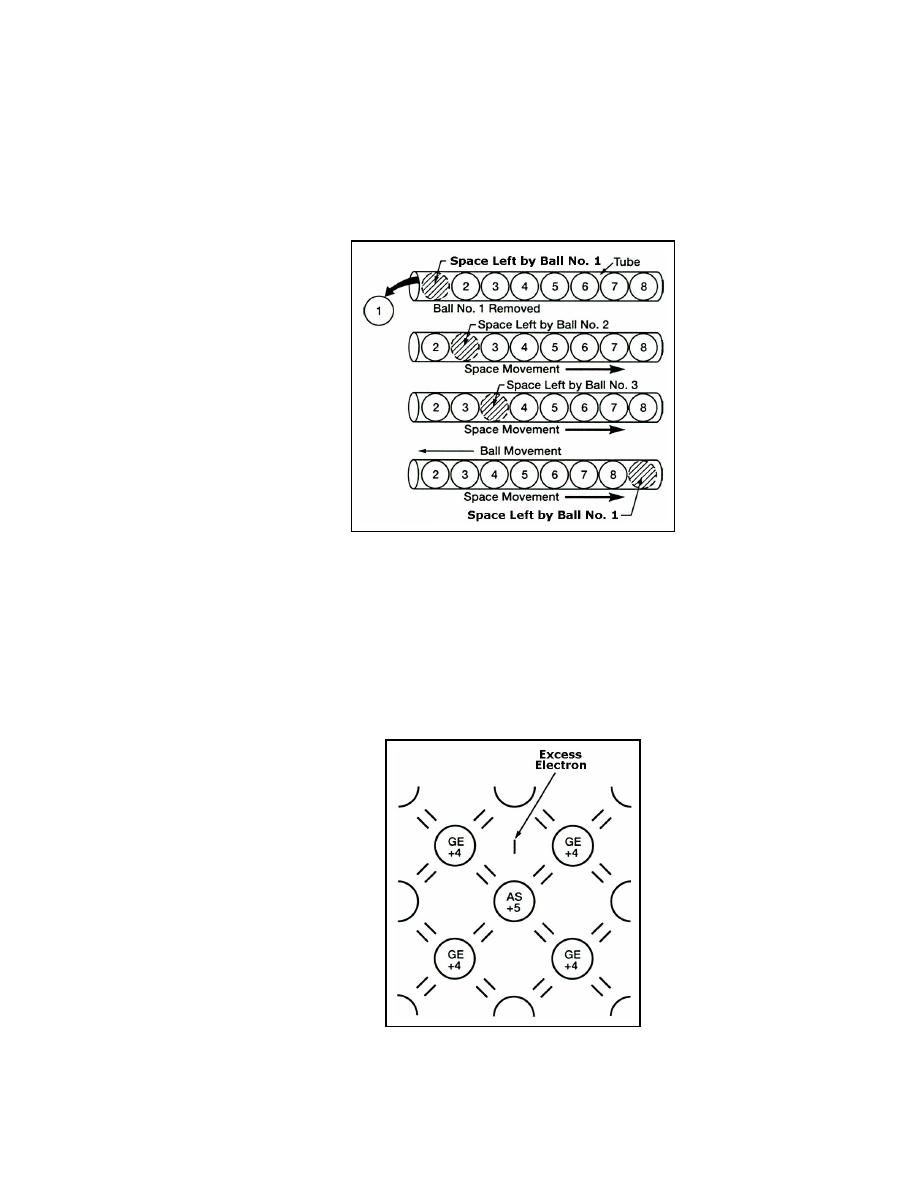
N-TYPE SEMICONDUCTOR - one that is doped with an N-type or donor
impurity (an impurity that easily loses its extra electron to the semiconductor
causing it to have an excess number of free electrons). Since this type of
semiconductor has a surplus of electrons, the electrons are considered the
majority current carriers while the holes are the minority current carriers.
P-TYPE SEMICONDUCTOR - one that is doped with a P-type or acceptor
impurity (an impurity that reduces the number of free electrons causing more
23 June 2005
TC 9-62
1-37



 Previous Page
Previous Page
