_________________________________________________________________ Semiconductor Diodes
of the electron. However, the mass of the proton is approximately 1,837 times
that of the electron.
neutron is approximately equal to that of the proton.
ELECTRON'S ENERGY LEVEL - the amount of energy required by an electron
to stay in orbit. Just by the electron's motion alone, it has kinetic energy. The
electron's position in reference to the nucleus gives it potential energy. An
energy balance keeps the electron in orbit and as it gains or loses energy, it
assumes an orbit further or closer to the center of the atom.
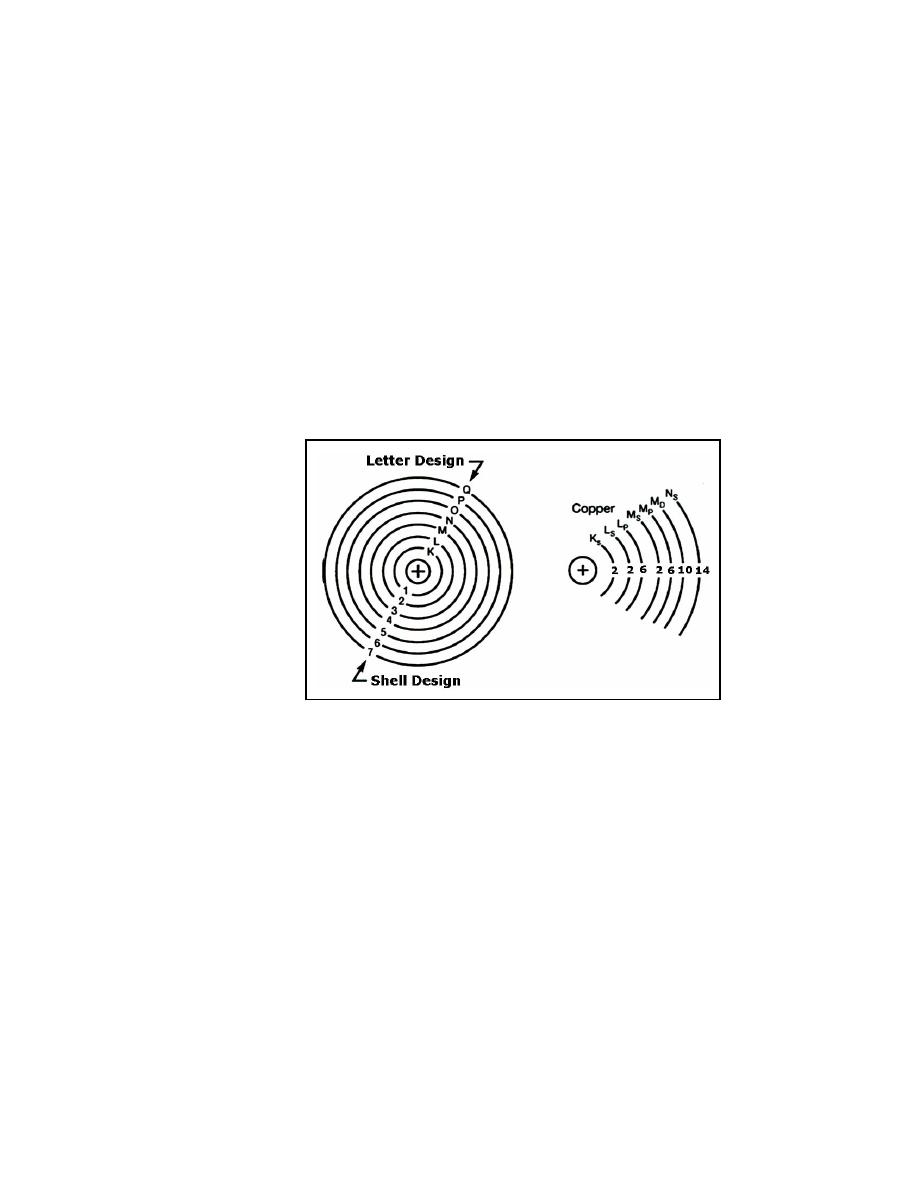
SHELLS AND SUBSHELLS - the orbits of the electrons in an atom. Each shell
can contain a maximum number of electrons that can be determined by the
formula 2N2. Shells are lettered K through Q (starting with K, which is the
closest to the nucleus). The shell can also be split into four subshells labeled s,
p, d, and f, which can contain 2, 6, 10, and 14 electrons, respectively.
VALENCE - the ability of an atom to combine with other atoms. The valence of an
atom is determined by the number of electrons in the atom's outermost shell.
This shell is referred to as the VALENCE SHELL. The electrons in the
outermost shell are called VALENCE ELECTRONS.
IONIZATION - the process by which an atom loses or gains electrons. An atom
that loses some of its electrons in this process becomes positively charged and
is called a POSITIVE ION. An atom that has an excess number of electrons is
negatively charged and is called a NEGATIVE ION.
23 June 2005
TC 9-62
1-35



 Previous Page
Previous Page
