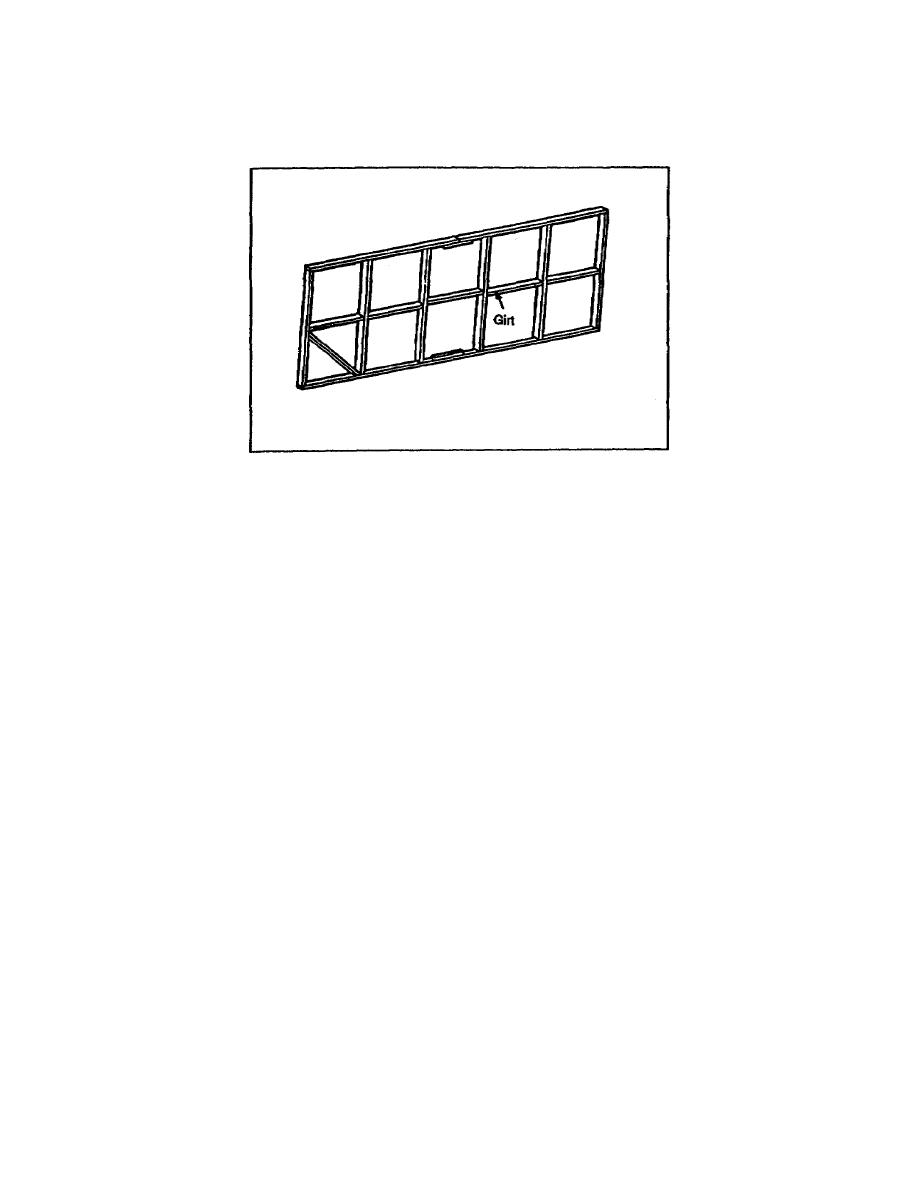
b. Sidewall Panels. Place studs from 2 to 10 feet apart, with girts placed horizontally between
the studs to construct sidewalls (see Figure 2-20). Vertical siding is normally used in this type of
construction.
Figure 2-20. Sidewall panels
PART B - WALL SHEATHING
After completing the framework of a building, fasten a covering, known as sheathing, to it. Sheathing
includes exterior wall sheathing, finish siding, and interior wall sheathing.
2-11. Exterior Wall Sheathing. Sheathing is nailed directly onto the framework of the building. It is
used to strengthen the building; provide a base wall to which finish siding can be nailed; act as
insulation; and, in some cases, be a base for further insulation. Some common types of sheathing
include wood, gypsum board, and plywood.
a. Wood Sheathing. Wood sheathing may be nailed on horizontally or diagonally (see Figure 2-
21) however, diagonal application adds much greater strength to the structure. If the sheathing is to be
put on horizontally, start at the foundation and work toward the top. If it is to be put on diagonally,
start at the corner of the building and work toward the opposite wall.
b. Gypsum Board. The long edges of the 4 by 8 boards are tongue-and-grooved. Gypsum
board can be nailed (together with the wood siding) directly to the studs. Gypsum sheathing is
fireproof, water resistant, and windproof. It does not warp or absorb water and does not require the use
of building paper (see Figure 2-22).
EN5156
2-14



 Previous Page
Previous Page
