2-2. Tooth-Cutting Tools. Both manually operated saws and power saws
are toothcutting tools.
a. Types of ToothCutting Tools. Manually operated saws used by
carpenter's are mainly the crosscut saw, ripsaw, compass saw, coping
saw, hacksaw, and miter saw.
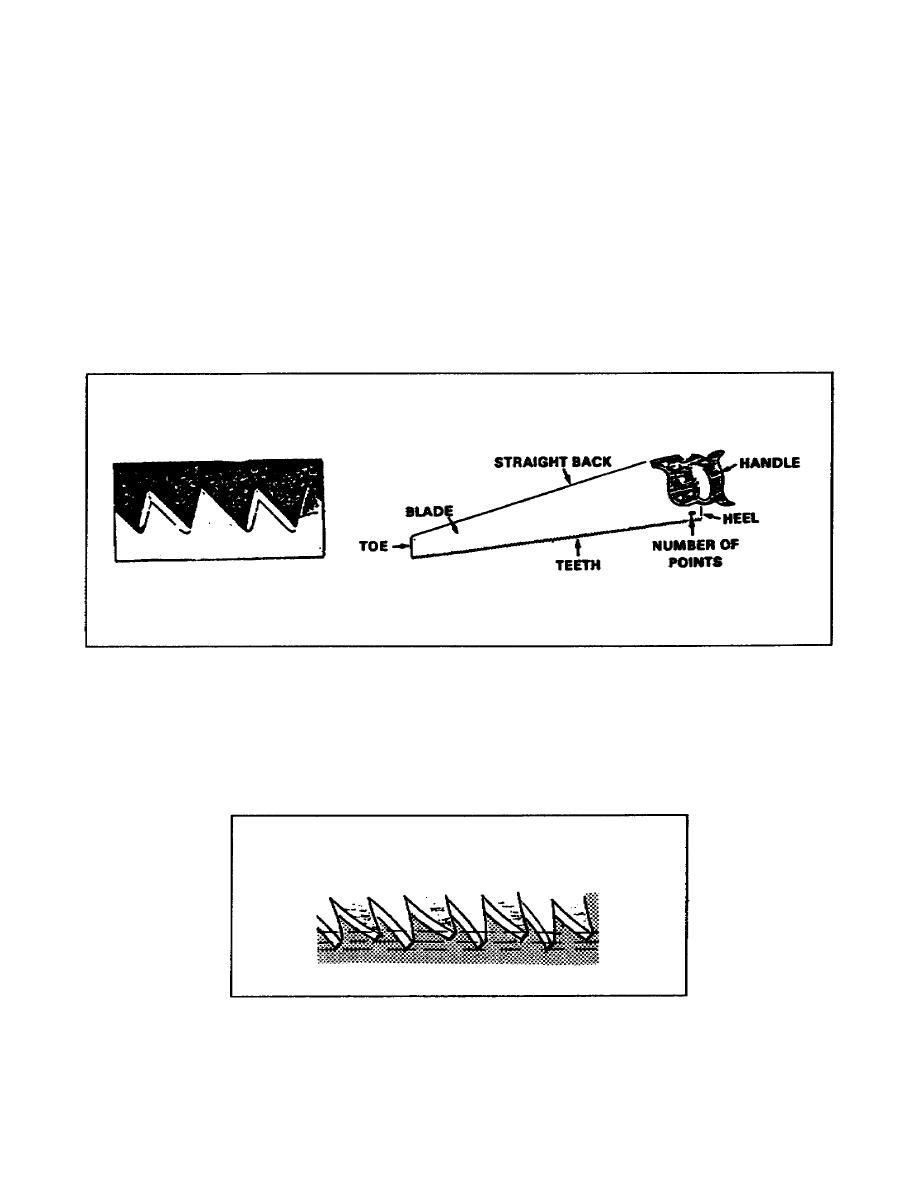
(1) Crosscut Saw. A crosscut saw (handsaw) (Figure 26) is
designed to cut across the grain of the wood. Its teeth are
sharpened like a knife so they will cut the fibers of the wood on
each side of the saw cuts (or kerf). A crosscut saw is 20 to 26
inches long and has 8 to 12 teeth per inch. The number of teeth per
inch is stamped on the blade near the handle.
Figure 2-6.
Crosscut saw
(2) Ripsaw. This saw is used to cut with (or parallel to) the
grain of the wood. The teeth of a ripsaw (Figure 27) are a series
of little chisels set in two parallel rows. On each full stroke of
the saw, the edges chisel off a little from the end of the wood
fibers. This cut is also called a kerf.
Figure 2-7.
Ripsaw teeth
EN5155
2-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
