2-9. Measuring Tools. The most used and important tools that you
must learn to use are those for measuring and layout work.
Carpenter's measuring tools include rulers and tapes. Layout tools
include various types of squares, dividers, and compasses and a
marking gauge. The square is used for drawing angles. Dividers and
compasses are used to scribe circles or transfer measurements. The
carpenter's scribe is in the same class as a compass; it is used to
scribe lines on building material for irregular joints. The marking
gauge is used to mark lines parallel to a surface, an edge, or the
end of a piece of lumber. Measuring and layout must be accurate;
therefore, use a very sharp pencil or a knife blade.
When measuring, lay out your ruler or tape from your starting point
and measure the distance called for by your plan. Place a mark
opposite the required distance and square or angle the line as
required by your layout.
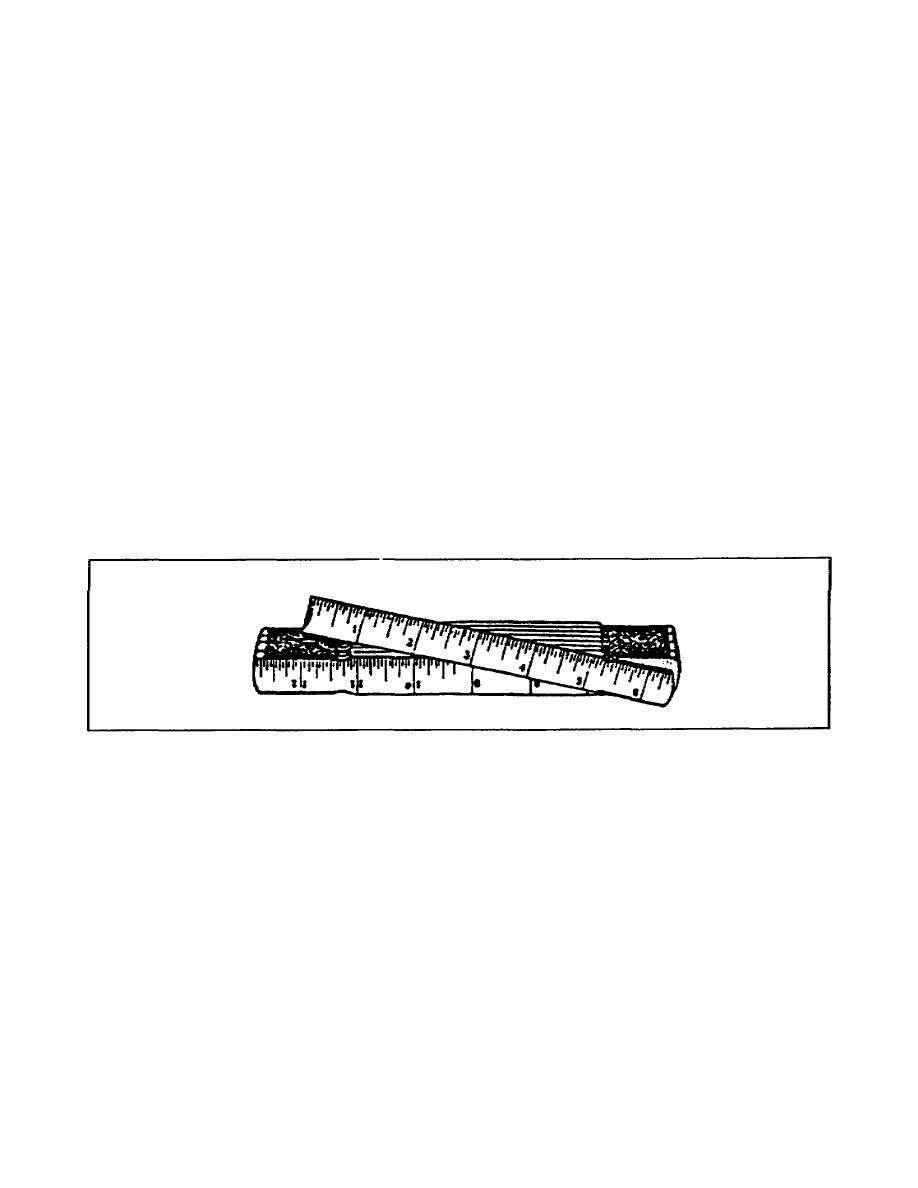
a. Folding Rule. A folding rule is made from boxwood and has a
concealed joint or rivet that holds it stiff and rigid when opened.
Usually 6 feet in length, it is marked off in feet and inches and
graduated in sixteenths of an inch. Figure 243 shows the folding
rule most often used by carpenters.
Figure 2-43.
Folding rule
b. Steel Tape. In recent years, the flexible steel tape has been
replacing the folding rule. It is also marked off in feet and inches
and graduated in sixteenths of an inch. The flexible steel tape is
housed in a metal casing with a spring attachment, which retracts the
tape into the casing when the end is released. This type of rule is
best because of its compactness and suitability for taking inside
measurements (Figure 244).
EN5155
2-22



 Previous Page
Previous Page
