__________________________________________________________ Radio Wave Propagation
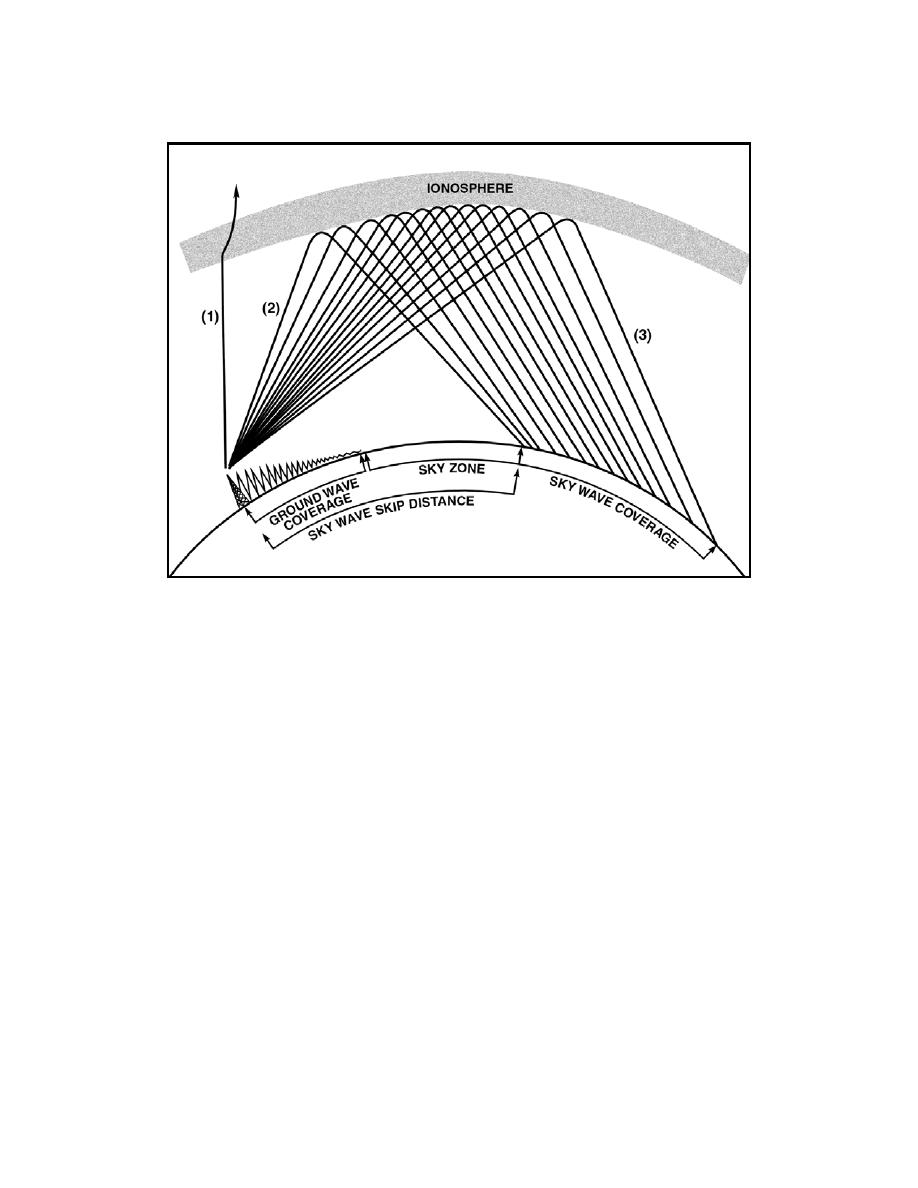
Figure 2-19. Relationship between Skip Zone, Skip Distance, and Ground Wave
Propagation Paths
2-73. The path that a refracted wave follows to the receiver depends on the
angle at which the wave strikes the ionosphere. You should remember,
however, that the RF energy radiated by a transmitting antenna spreads out
with distance. The energy therefore strikes the ionosphere at many different
angles rather than a single angle.
2-74. After the RF energy of a given frequency enters an ionospheric region,
the paths that this energy might follow are many. It may reach the receiving
antenna via two or more paths through a single layer. It may also, reach the
receiving antenna over a path involving more than one layer, by multiple
hops between the ionosphere and Earth, or by any combination of these
paths.
2-75. Figure 2-20 shows how radio waves may reach a receiver via several
paths through one layer. The various angles at which RF energy strikes the
layer are represented by dark lines and designated as rays 1 through 6.
2-25



 Previous Page
Previous Page
