________________________________________________________________Wave Propagation
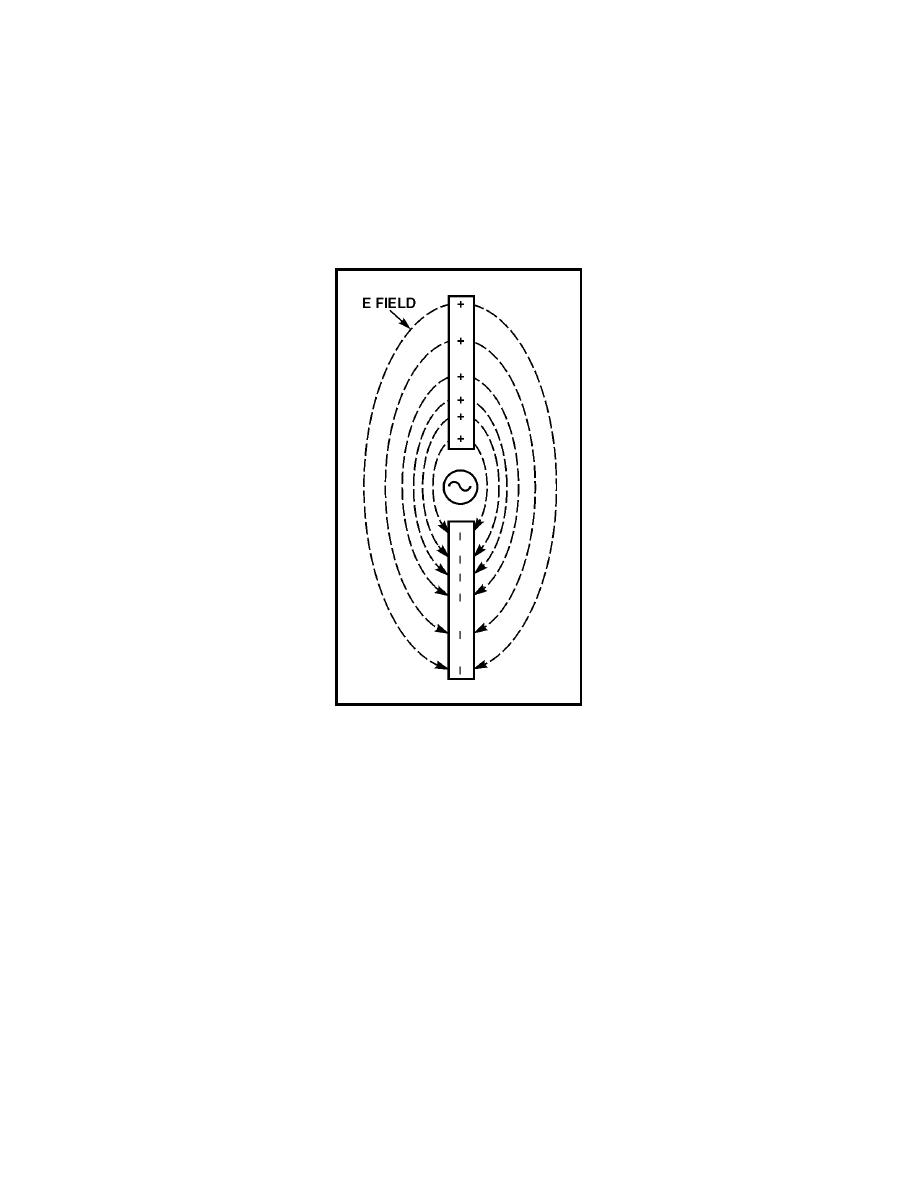
1-125. In figure 1-27, two rods replace the plates of the capacitor, and the
battery is replaced by an AC source generating a 60-hertz signal. On the
positive alternation of the 60-hertz generator, the electric field extends from
the positively charged rod to the negatively charged rod, as shown. On the
negative alternation, the charge is reversed. The previous explanation of
electrons moving from one plate to the other of the capacitor in figure 1-25
can also be applied to the rods in figure 1-27.
Figure 1-27. Electric Fields between Elements
1-126. The polarity of charges and the direction of the electric fields will
reverse polarity and direction periodically at the frequency of the voltage
source. The electric field will build up from zero to maximum in one direction
and then collapse back to zero. Next, the field will build up to maximum in
the opposite direction and then collapse back to zero. This complete reversal
occurs during a single cycle of the source voltage. The half-wave dipole
antenna (two separate rods in line as illustrated in figure 1-27) is the
fundamental element normally used as a starting point of reference in any
discussion concerning the radiation of electromagnetic energy into space. If
RF energy from the AC generator (or transmitter) is supplied to the element
of an antenna, the voltage across the antenna lags the current by 90 degrees.
The antenna acts as if it were a capacitor.
Magnetic Field
1-127. When current flows through a conductor, a magnetic field is set up in
the area surrounding the conductor. In fact, any moving electrical charge will
create a magnetic field. The magnetic field is a region in space where a
1-37



 Previous Page
Previous Page
