______________________________________________________________ Solid State Power Supplies
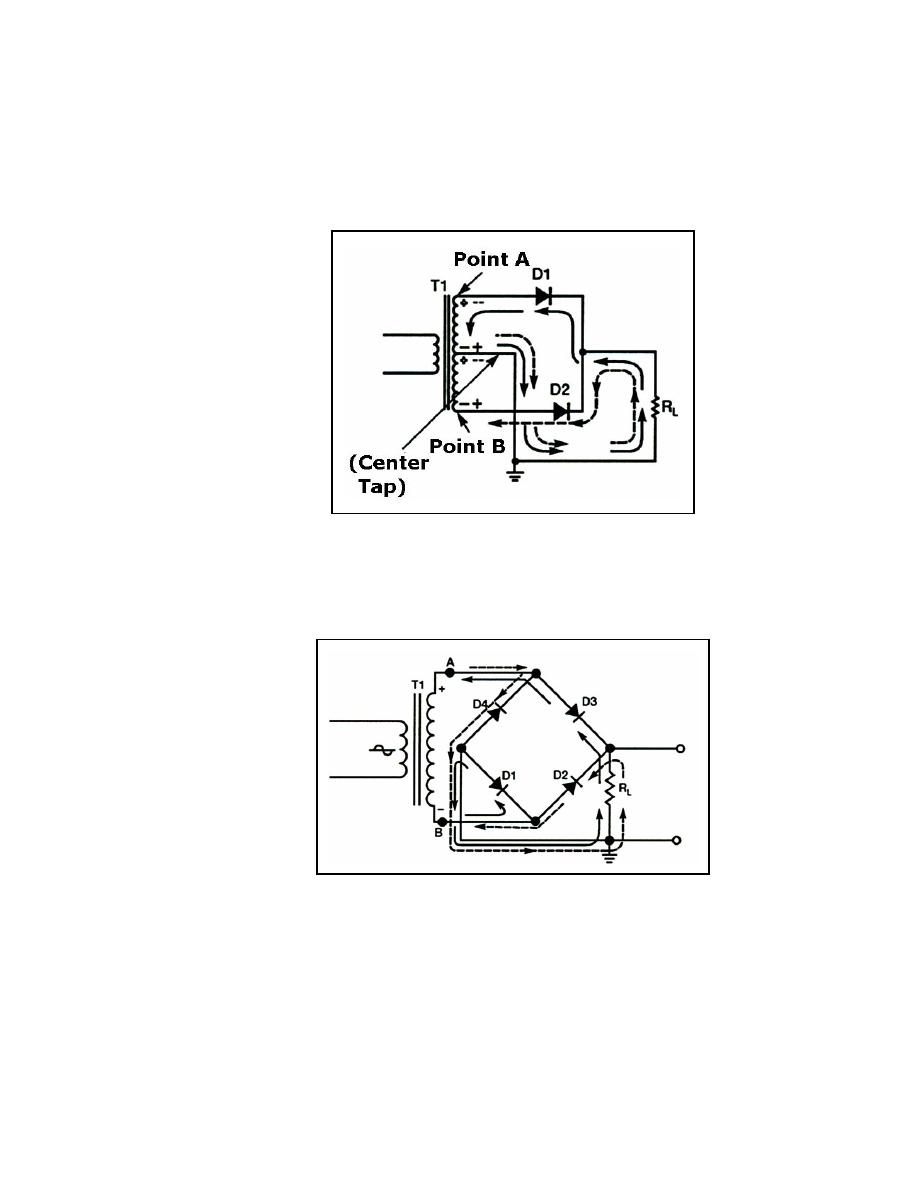
FULL-WAVE RECTIFIERS - conducts on both halves of the input AC cycles. As
a result, the DC pulses are not separated from each other. A characteristic of
full-wave rectifiers is the use of a center-tapped, high-voltage secondary.
Because of the center tap, the output of the rectifier is limited to one-half of the
input voltage of the high-voltage secondary.
BRIDGE RECTIFIERS - full-wave rectifiers that do not use a center-tapped,
high-voltage secondary. Because of this, their DC output voltage is equal to
the input voltage from the high-voltage secondary of the power transformer.
Bridge rectifiers use four diodes connected in a bridge network. Diodes
conduct in diagonal pairs to give a full-wave pulsating DC output.
FILTER CIRCUITS - designed to smooth, or filter, the ripple voltage present on
the pulsating DC output of the rectifier. An electrical device, that has the
ability to store energy and to release the stored energy, can do this.
23 June 2005
TC 9-62
4-49



 Previous Page
Previous Page
