For example, if c is 15 meters and M is 2 meters, compute the radius of curvature as
follows:
15 2
2
225
R=
+
=
+ 1 = 14.0625 + 1 = 15.0625 = 15 meters
8 2
2
16
The result shows that the radius of curvature is an obstruction to traffic flow. The curve
symbol is marked at the site of the curve on the map overlay, and OB is annotated in the
route classification formula.
PART B BODIES OF WATER
Bodies of water may also present obstructions to military traffic. Some of the information
that needs to be gathered for bodies of water includes depth, width, velocity, composition of
the stream bottom, and possible military water points.
1-3. Water Fractures. Because modern military vehicles have built-in stream-crossing
capabilities, a commander can more efficiently conduct vehicular fording, swimming, and
ferrying operations. To assist the commander, reconnaissance personnel locate and report
stream-crossing sites that are likely to permit smooth traffic flow and reduce route
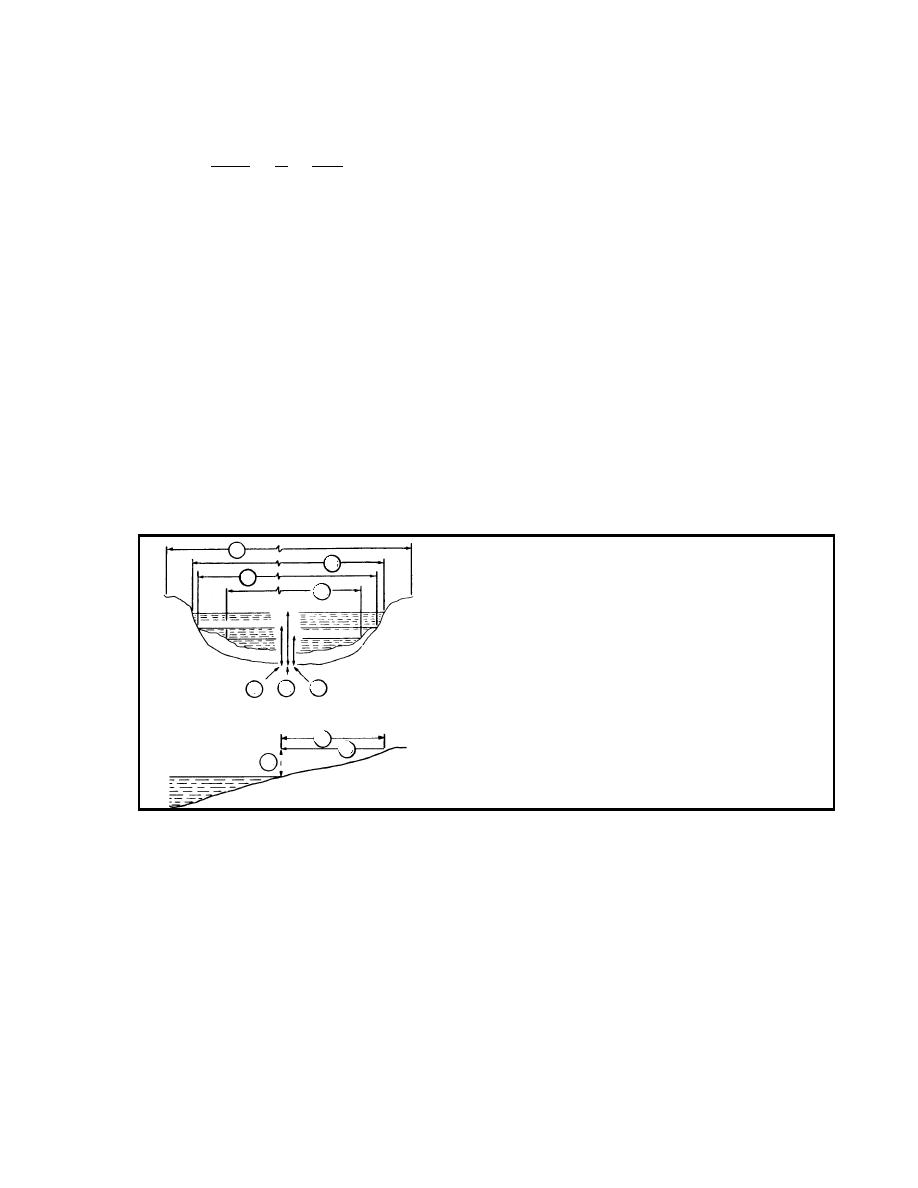
obstructions as much as possible (Figure 1-8).
1
2a
1. The width of the streambed from bank to bank.
2
2. The actual width of the water, measured at
2b
normal stage. The maximum width (2a) and the
minimum width (2b) are estimated based on local
observations or records of high water and low
water.
3. The actual depth of the stream, measured at
normal water level. The maximum water depth
3b
3
3a
(3a) and the minimum water depth (3b) are
estimated based on local observations or records.
4. The slope of the approach is the slope of the
4
stream banks through which the approach roads
4b
are cut (4a is the approach elevation, and 4b is
4a
the approach distance).
Figure 1-8. Dimensions Required for Reporting Streams
a.
Stream depth can usually be determined by using field-expedient devices (such
as measured poles or weighted ropes). Depth readings are normally taken every 3 meters.
In the event of a sudden heavy rainfall, depths must be checked at frequent intervals to
provide warning of possible sudden flooding. The actual depth at the time of reconnaissance
is recorded as the normal depth during a hasty reconnaissance.
b.
Stream width can be measured using several methods. Measure short gaps by
having a member of the reconnaissance team hold the end of a tape measure or rope on the
near bank. Have another member of the team cross to the opposite bank and pull the tape
1-7
EN 5622



 Previous Page
Previous Page
