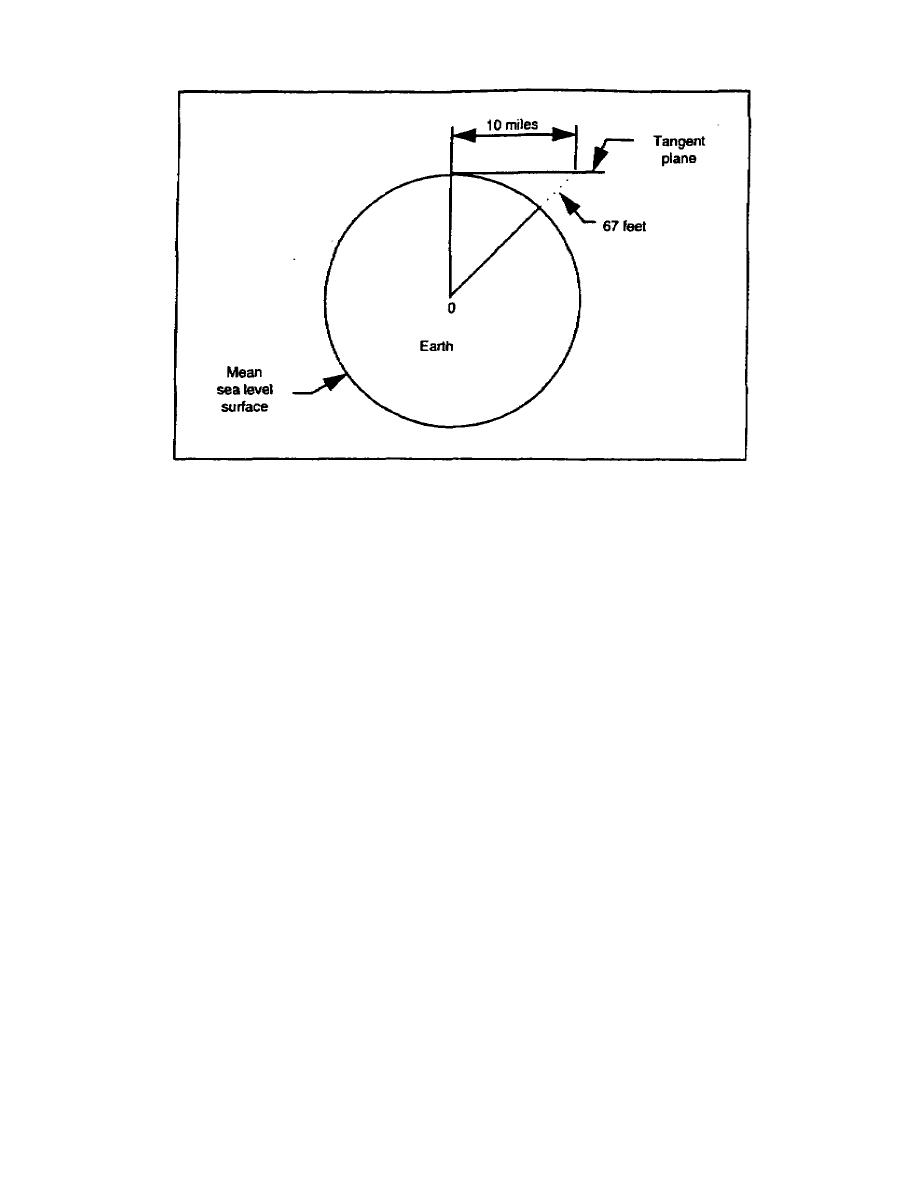
Figure 1-3. The effect of the earth's curvature
Blaze-A mark made on the trunk of a standing tree by chipping off a spot of bark with an ax. It
is used to indicate a trail, a boundary, a location for a road, a tree to be cut, and so on.
Bubble axis (level vial)-The horizontal line tangent to the upper surface of the centered bubble,
which lies in the vertical plane through the longitudinal axis of the bubble tube.
from a standard so as to ascertain the proper correction factors.
proper position relative to the other parts of the instrument.
telescope and the center of the reticle. It is also referred to as the line of sight, sight line,
pointing line, and the aiming line of the instrument. The center of the telescope reticle can be
defined by the intersection of crosshairs or by the middle point of a fixed vertical wire or a
micrometer wire in its mean position. In a leveling instrument, the center of the reticle may be
the middle point of a fixed horizontal wire.
Contour-An imaginary level line (constant elevation) on the ground surface; it is called a
contour line on a corresponding map.
Datum-Any numeric or geometric quantity that serves as a reference or base for other
quantities. It is described by such names as geodetic, leveling, North American, or tidal datum,
depending on its purpose when established.
EN0591
1-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
