better suited to construction than temperate climate
are wide in the center, and narrow to nothing near the
trees. For example, they offer more resistance to
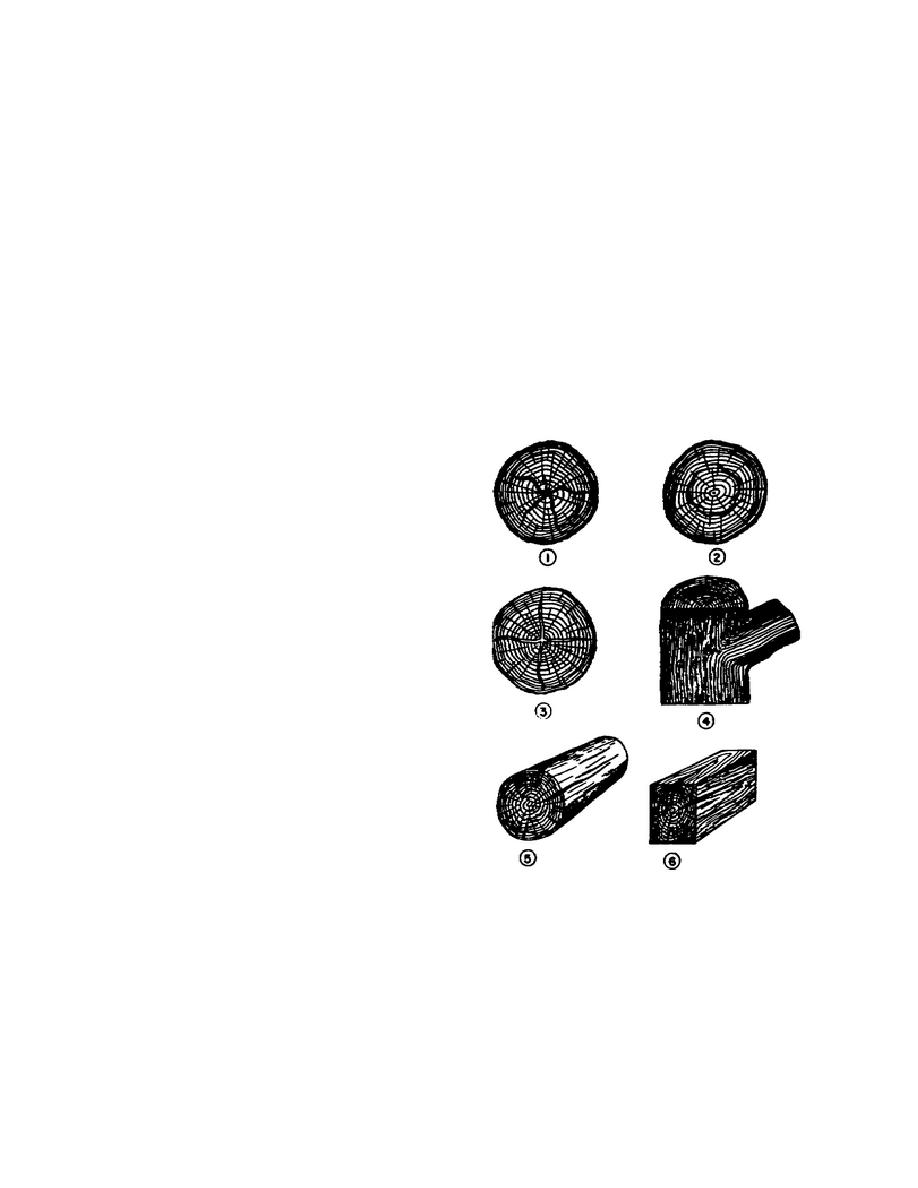
bark. The wood along these cracks is solid (3, fig. 1-
insects and decay. Because of its shape - a thin
13).
hollow column - bamboo has been called the ideal
d. Knots. Knots are irregular growths in
building material. Lack of a simple method of
the body of a tree which interrupt the smooth curve
satisfactorily connecting such members is its major
of the grain. The fibers of the tree are turned from
short-coming. Both palm and bamboo have been
their normal course and grow around the knot at that
used extensively by the Army.
point of a tree where a limb is being formed. If the
knot is large, cross grains are formed which cause the
1-11. SEASONING
lumber to break easily (4, fig. 1-13).
Seasoning of lumber is the controlled drying or
removal of moisture from wood. Seasoning increases
Checks are splits in the
e. Checks.
the strength of timber, improves its resistance to
outside part of a piece of timber which are caused by
decay, and minimizes shrinkage and warping of
irregular shrinkage. Checks are formed when the
structural members. Since dry lumber is lighter, the
circumference shrinks more than the interior section
dead weight of a structure is reduced by using
of the wood (5, 6, fig. 1-13).
seasoned timber. Although seasoned lumber is
preferred for construction purposes, "green" timber
may be used with good results for almost any TO
type building. The only item for which green wood
cannot be used satisfactorily in TO construction is
sheathing. When green sheathing dries out after
being covered with roll roofing, it shrinks and tears
holes in the roofing material where the nails are
inserted.
1-12. DEFECTS
In the growth and life of a tree certain defects
occur which weaken timber cut from these trees. The
defects are classed as heartshakes, windshakes,
starshakes, knots, and checks.
a. Heartshake or heart rot. Heartshake
is a defect of .the heartwood found in older trees,
especially the hemlock; it is seldom found in
saplings. The heartshake is evidenced by a small
round cavity at the center of the tree or timber. This
cavity is caused by decay and results in cracks which
extend outward to the bark (1, fig. 1-13).
b. Windshake.
Windshake is the
separation of the annual rings (2, fig. 1-13). This
defect is most common in pine timber. Windshakes
sometimes extend several feet up the trunk of a tree.
c. Starshake. A starshake is much like a
Figure 1-13. Defects in timber.
heartshake in its effect. The difference between the
two is that the starshake has no decay at the center.
The cracks extend over the cross section of the log,
1-16



 Previous Page
Previous Page
