TC 9-64 _________________________________________________________________________
A source can be anything that emits or expends energy (waves).
The medium is the vehicle for carrying waves from one point to another.
Water, air, metal, and empty space are examples of mediums. Empty space
can serve as a medium for electromagnetic waves but not for sound waves.
The sound detector absorbs the waves emitted by the source. The human ear
is an example of a detector.
Hertz, which is abbreviated Hz, is used in lieu of "cycle per second" when
referring to radio frequencies.
Velocity of propagation is the speed (or rate) at which the crest of a wave
moves through a medium. Velocity can be calculated by using the formula:
v = λf
Where v is velocity of propagation and is expressed in feet (meters) per
second, λ is the wavelength in feet (meters), and f is the frequency in hertz.
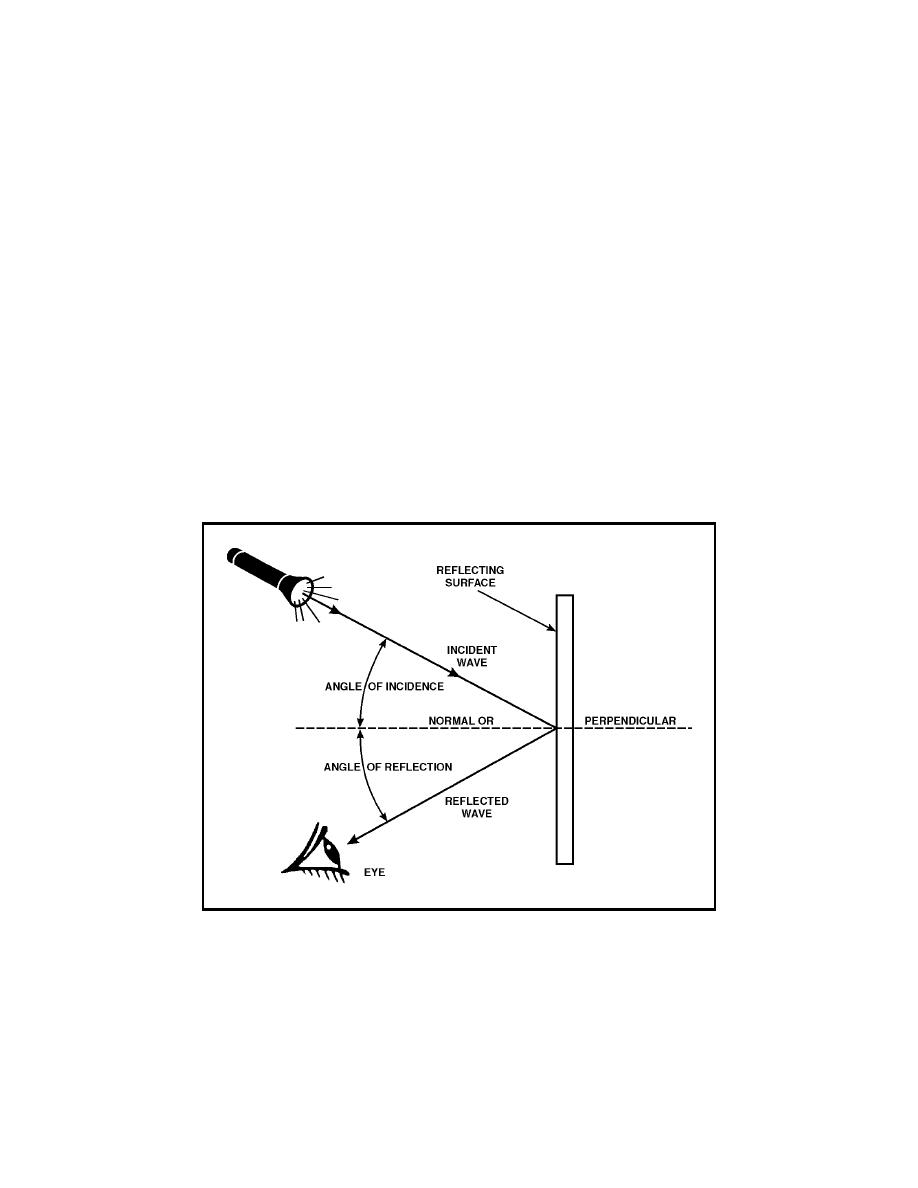
Reflection occurs when a wave strikes an object and bounces back (toward the
source). The wave that moves from the source to the object is called the
incident wave, and the wave that moves away from the object is called the
reflected wave.
Figure 1-Sum 4. Reflection of a Wave
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of
reflection.
Refraction occurs when a wave traveling through two different mediums
passes through the boundary of the mediums and bends toward or away from
the normal.
1-42



 Previous Page
Previous Page
