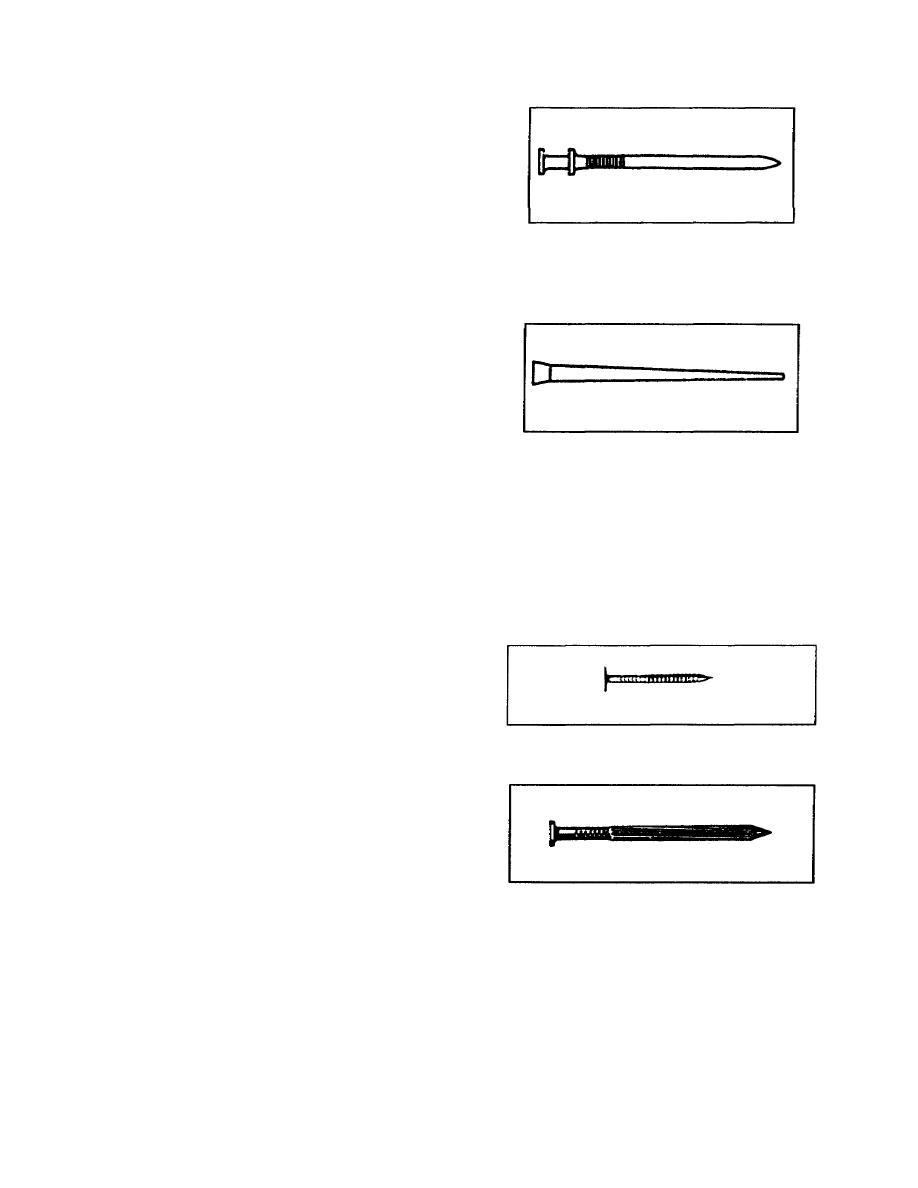
(e) DuplexHead
or
DoubleHeaded Nails. Duplex
head or doubleheaded nails
(Figure 128) are used in
temporary construction such as
form work and scaffolding. The
advantage of using this type of
nail is easy removal. It has a
Figure 1-28. Duplex-head or
collar that keeps the head away
double-headed nail
from the wood, and the claw of
the hammer can easily engage the
head for removal.
(2) Cut Nails. Cut nails
are wedgeshaped with a head on
the large end (Figure 129).
They are often used to nail
flooring because they have good
holding power and are made of
Figure 1-29.
Cut nail
very hard steel.
(3) Special Nails. Rustproof nails are sometimes used when the
head is exposed to the weather. The head often rusts and causes a
black streak along the grain of the wood, even though it is painted.
Therefore, it is desirable to use a nail that will not rust. Plain
wire nails that have a zinc coating are often used where there is a
possibility of rusting. These are called galvanized nails (such as a
roofing nail).
(4) Drywall
Nails.
Drywall nails (Figure 130) are
used for hanging drywall and
have a special coating to
prevent rust.
Figure 1-30.
Drywall nail
(5) Masonry (Concrete)
Nails. Masonry nails (Figure 1
31) are available in lengths
from 1/2 inch to 4 inches, with
a single head. These nails are
usually hardened steel.
Concrete nails are thicker and
are used to fasten metal or wood
Figure 1-31.
Masonry nail
to masonry or concrete.
b. Sizes. Nail sizes are given by penny number from twopenny to
sixtypenny (Figure 132). A small letter d is the recognized
abbreviation for penny. The penny number refers to the length of the
nail. Nails are normally packaged in 50pound boxes. Table 17,
page 134, gives the general sizes and types of nails preferred for
specific applications.
EN5155
1-32



 Previous Page
Previous Page
