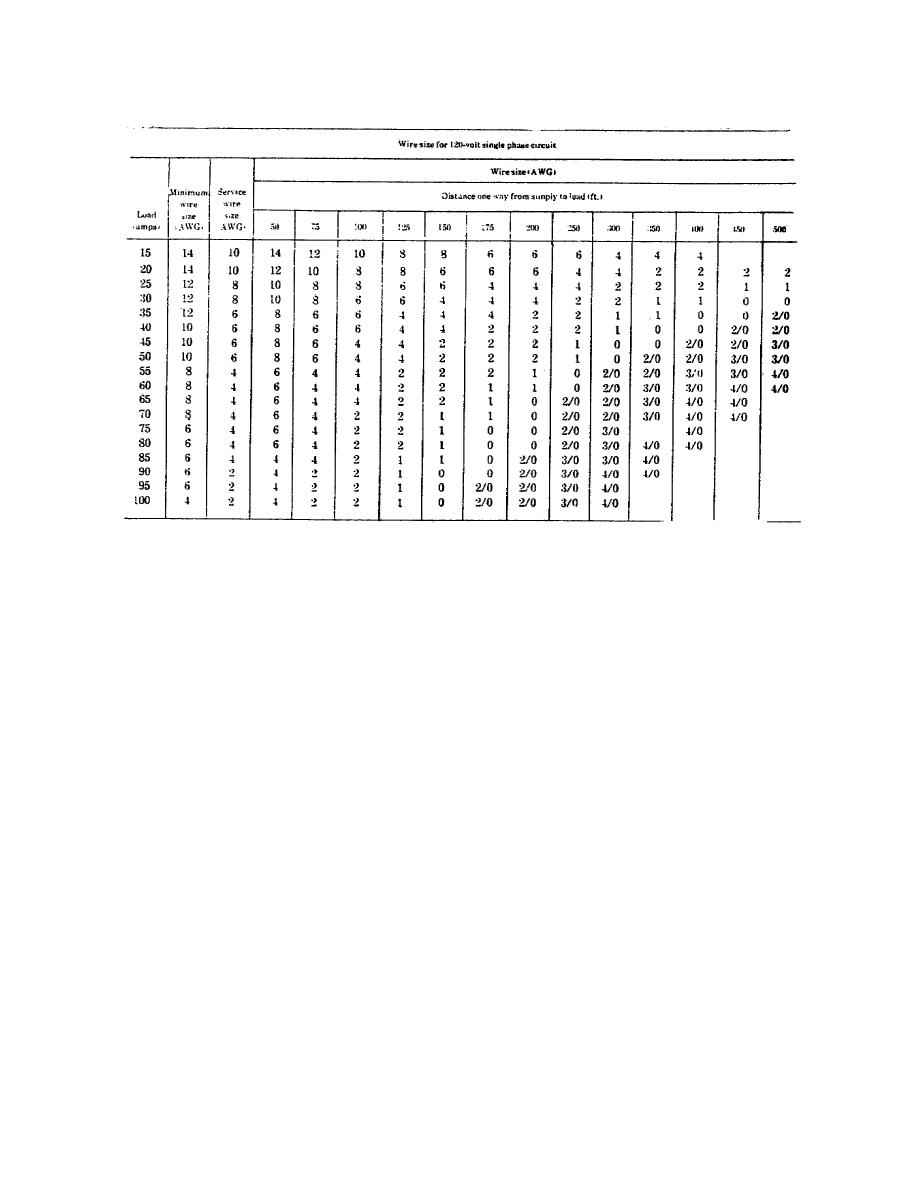
Table 3-9. Minimum Wire Sizes
too much time and would be impractical.
provisions. All connections and splices are made
Consequently, expedient wiring used for temporary
within boxes, usually with wire nuts. Cables are run
buildings and forward areas does not require the
through holes in building members or supported by
mounting and protective devices used in permanent
staples or straps. Nonmetallic sheathed cable is
installations. Generally, the wires are attached to
sometimes used for interior wiring also. Connections
building members with nails, and pigtail sockets are
and supports are similar to armored cable wiring.
tape is used as a protective covering on the
(4) Conduit wiring. Rigid of thin-wall
connections.
Fixture drops, preferably pigtail
conduit wiring provides the highest-quality, and most
sockets, are installed by tapping their leads to wires
expensive installation. Rigid or thin-wall pipe is used
and then taping the taps. The sockets are supported
to support and protect the conductors. Splices and
by the tap wires.
taps are made at junction boxes or outlet boxes. Very
little additional support or mechanical damage
(2) Open wiring. Open wiring is the type
protection is required beyond that provided by the
most often used in theater of operation construction
conduit.
because of economy of materials and ease of making
additions or alterations. Wiring is supported and
b. Fixtures. The various switches and outlets,
separated on porcelain knobs, cleats, and tubes or
such as lighting fixtures and receptacles, are shown
encased in a nonmetallic flexible casing called loom.
by symbols on interior wiring pins. The most
Wiring exposed to possible mechanical damage is
frequently encountered symbols are shown in figure
protected by running boards or railings. Taps or
332.
splices are supported.
c. Fuse Boxes and Circuit Breakers. Each
Armored
branch circuit is connected to some protective device,
(3) Armored cable wiring.
cable, commonly called BX, provides mechanical
usually at the point where
damage protection without additional protective
146



 Previous Page
Previous Page
