Lesson 1/Learning Event 2
Slow-Curing (SC). Composed of asphalt cement and diesel fuel, with a curing time of 48 to 60
hours.
Road-Oil. A heavy petroleum oil.
Grades of Asphalt Cutbacks
If a great amount of cutterstock is added to a given amount of asphalt cement, a very thin liquid will
result. Different amounts of cutterstock are added to a given amount of asphalt cement (AC) to obtain
various thicknesses or viscosity grades of cutbacks. A new set of specifications for asphalt cutbacks has
been approved by the Corps of Engineers. This specification covers the following types and viscosity
grades (Kinematic Viscosity):
Rapid-Curing (RC) -70,250,800,3000
Medium-Curing (MC) -30,70,250,800,3000
Slow-Curing (SC) - 70, 250, 800, 3000
ASPHALT EMULSIONS
It is often advantageous to use as asphalt material that is liquid at room temperature and yet will not
burn. Asphalt emulsions (emulsified asphalts) possess these properties.
Asphalt emulsions are composed of asphalt cement, water, and an emulsifier mixed together to produce
a liquid material. Asphalt and water will not mix alone so a chemical agent called an "emulsifying
agent" must be added. It is this emulsifying agent that enables the asphalt and water to mix. Common
emulsifying agents are soaps, animal blood, chemicals, and certain specified colloidal clays in dust.
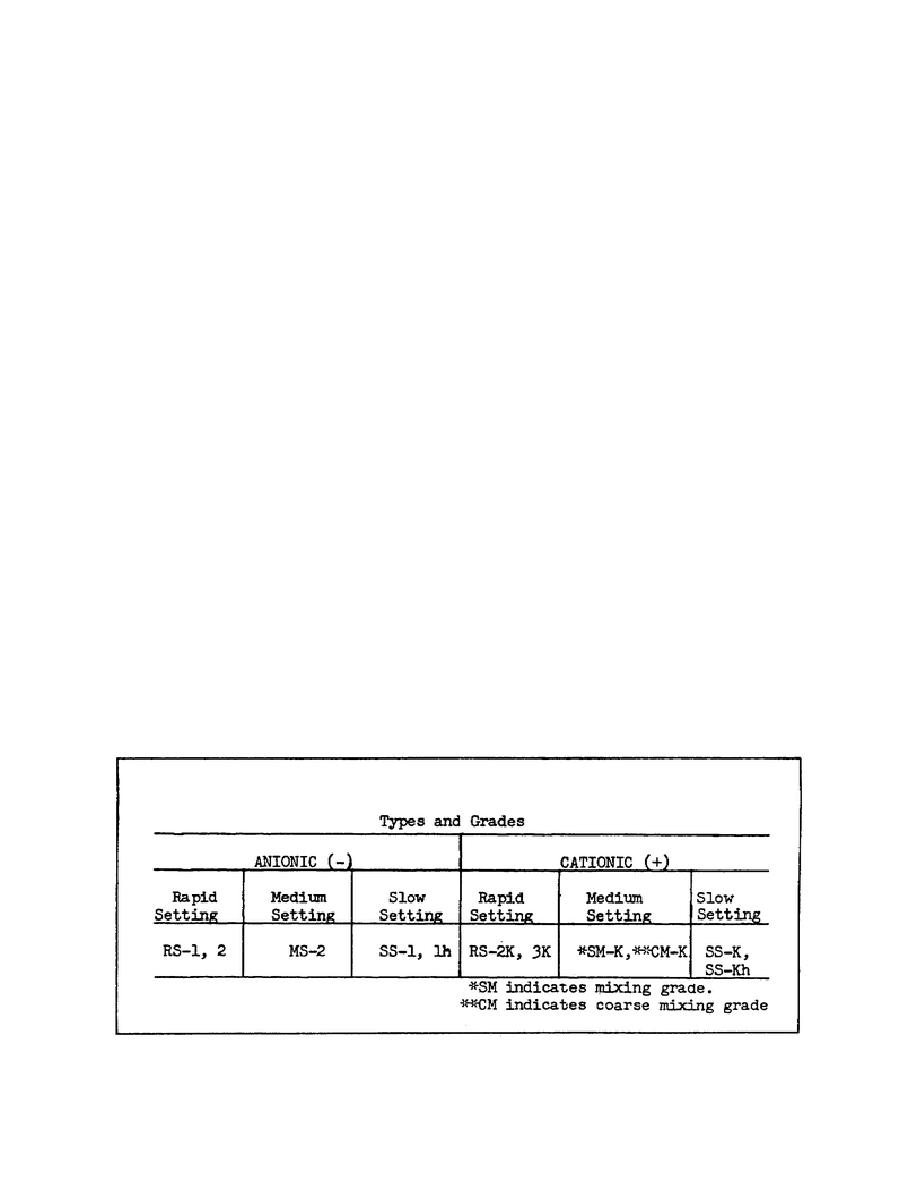
Emulsified asphalts may be of either the anionic electro (negatively) charged asphalt globules, or
cationic electro (positive) charged asphalt globules, depending upon the emulsifying agent.
TABLE 1. TYPES OF ASPHALT EMULSIONS
5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
