Lesson 3/Learning Event 2
of test holes, profile of the natural ground to scale, location of any ledge rock encountered, field
identification of each soil type, thickness of each soil stratum, and profile of the water table.
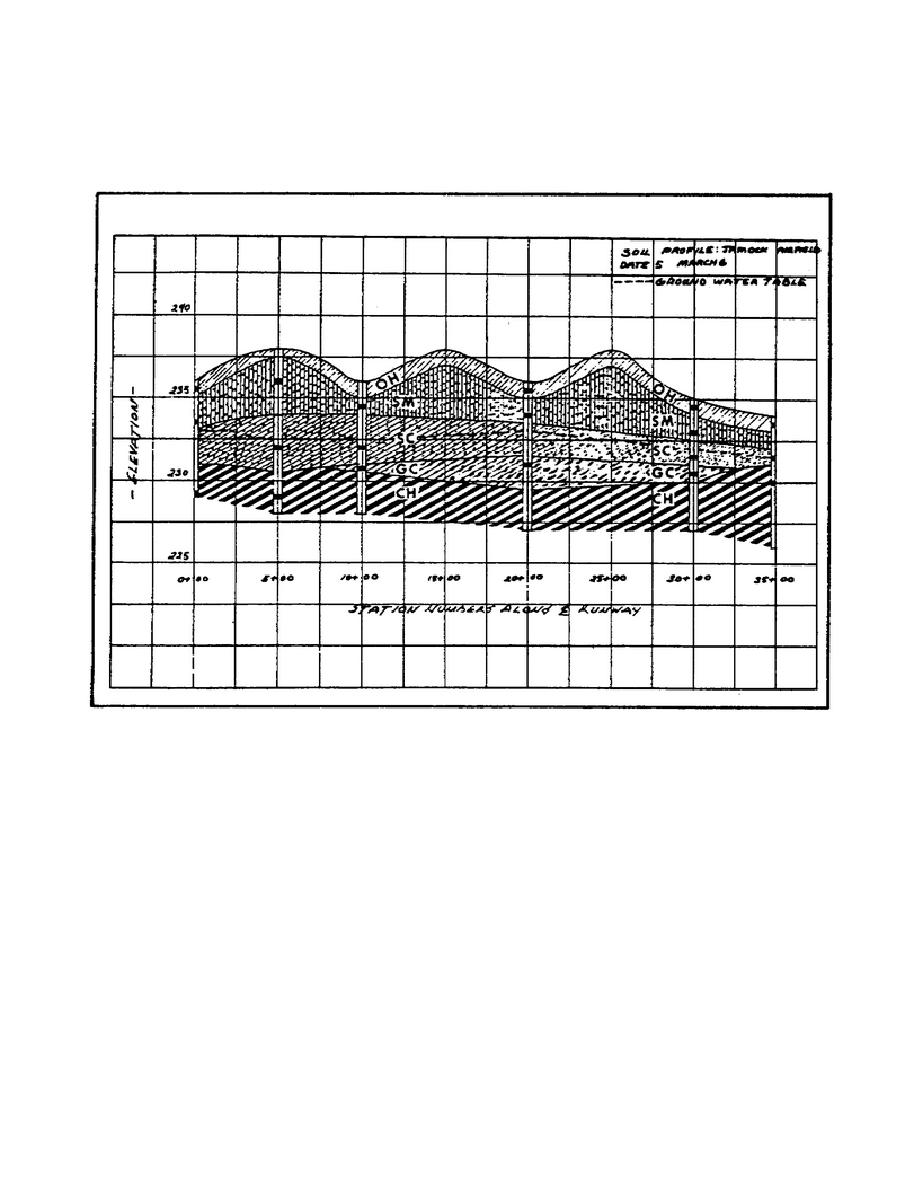
FIGURE 26. TYPICAL SOIL PROFILE
Uses of the Soil Profile
The soil profile has many practical uses in the location; design, and construction of roads, airfields, and
structures. It has a great influence in the location of the grade line, which should be placed so that full
advantage is taken of the best soils which are available at the site. The profile will show whether soils to
be excavated are suitable for use in embankments, or if borrow soils will be required. It may show the
existence of undesirable conditions, such as peat or organic matter or bedrock close to the surface, which
will require special construction measures. It will aid in the planning of drainage facilities so that
advantage may be taken of the presence of well-draining soils. It may indicate that special drainage
installations will be needed with soils which are more difficult to drain, particularly in areas where the
water table is high. Considerations relative to capillary and frost action may be particularly important
when frost-susceptible soils are shown on the profile.
72



 Previous Page
Previous Page
