Lesson 3/Learning Event 2
Sampling Methods
The following paragraphs describe the conventional methods of subsurface sampling.
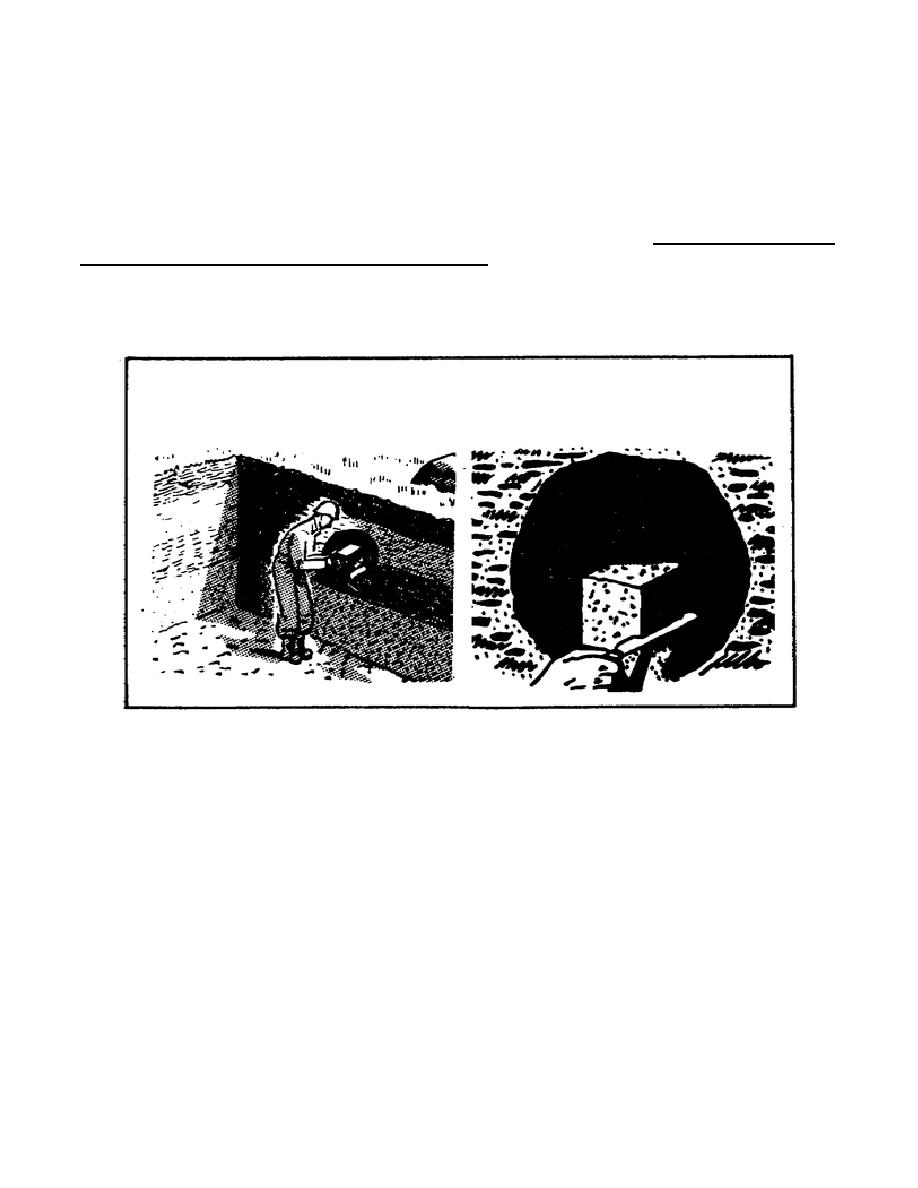
Test Pits. A test pit is an open excavation which is large enough for a man to enter and study the soil in
its undisturbed condition. This method provides the most satisfactory results for observing the natural
condition of the soil and collecting undisturbed samples. The test pit usually is dug by hand but power
excavation by dragline, clamshell, bulldozer, backhoe, or a power-driven earth auger can expedite the
digging. Load bearing tests can also be performed on the soil in the bottom of the pit. Figures 23 shows
a soldier taking a chunk sample in a test pit.
FIGURE 23. TAKING A CHUNK SAMPLE
FROM A VERTICAL FACE
Test Holes. Test hole exploration includes several methods as described below.
Hand Auger. The use of the hand auger is the most common method of digging test holes. It is
best suited to cohesive soils but can be used on cohesionless soils above the water table, provided the
diameter of the individual aggregate particles is smaller than the bit clearance of the auger. The auger
borings are principally used for work at shallow depths. By adding pipe extensions, the earth auger may
be used to a depth of about 30 feet in relatively soft soils. The sample is completely disturbed and is
satisfactory for determining the soil profile, classification, moisture content, compaction capabilities,
and similar properties of the soil. Figure 24 shows a soldier obtaining samples with a hand auger.
66



 Previous Page
Previous Page
