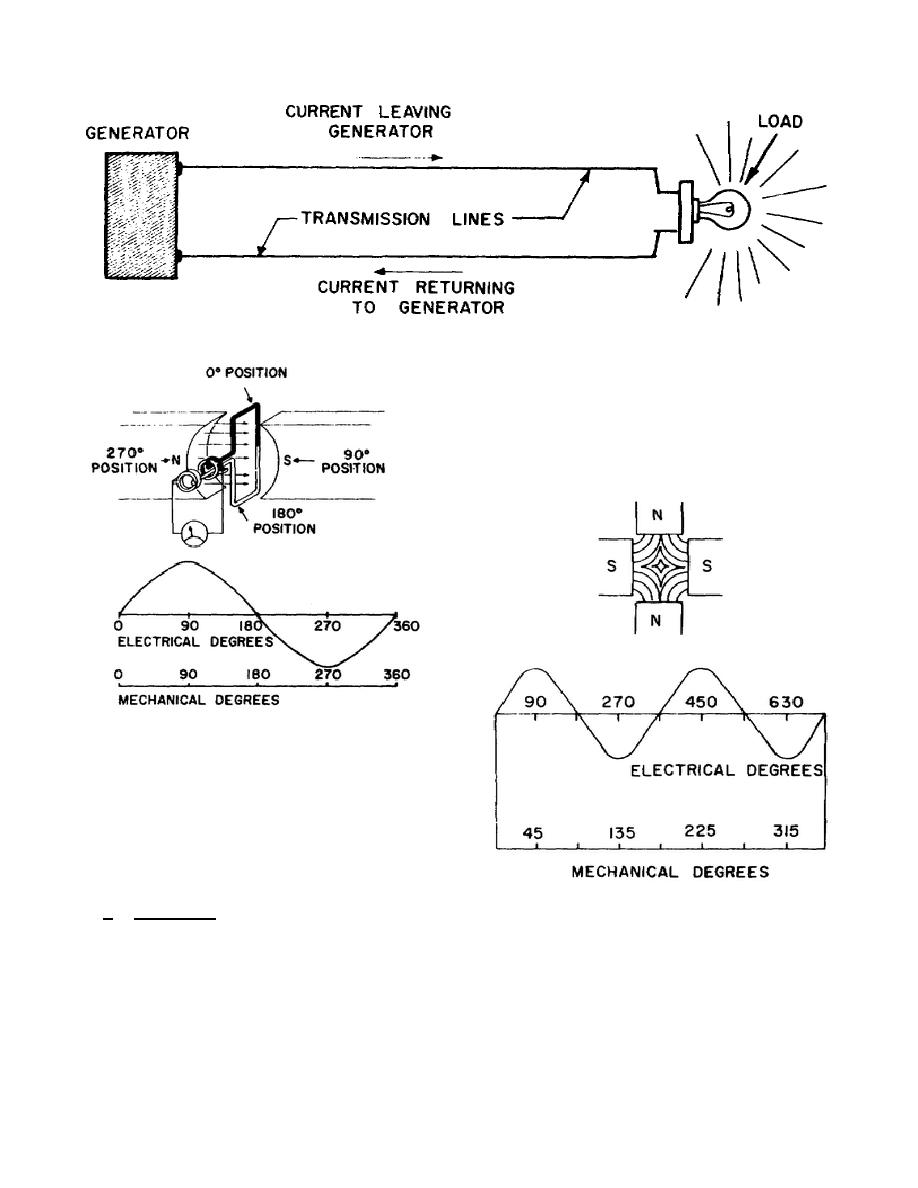
Figure 1.
to
rotate
at
3,600
revolutions
per minute to produce a frequency of
60 cycles per second.
A more common
type of generator in use today is
the multipole generator which produces
alternating
current
at
a
much
slower
rpm.
Figure
3
shows
a
Figure 2.
Simple two-pole AC
generator.
the loop reaches the 180-degree point,
it is no longer cutting any lines and
the current is zero.
One complete
revolution of the loop constitutes one
cycle because the current has gone
from zero to maximum value twice as
shown in figure 2.
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of four-
b. Frequency.
The
number
of
pole AC generator.
cycles
per
second
is
expressed
as
frequency.
The
most
common
frequency
in
use
in
the
United
States is 60 cycles per second.
A
simple two-pole generator would have
1-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
